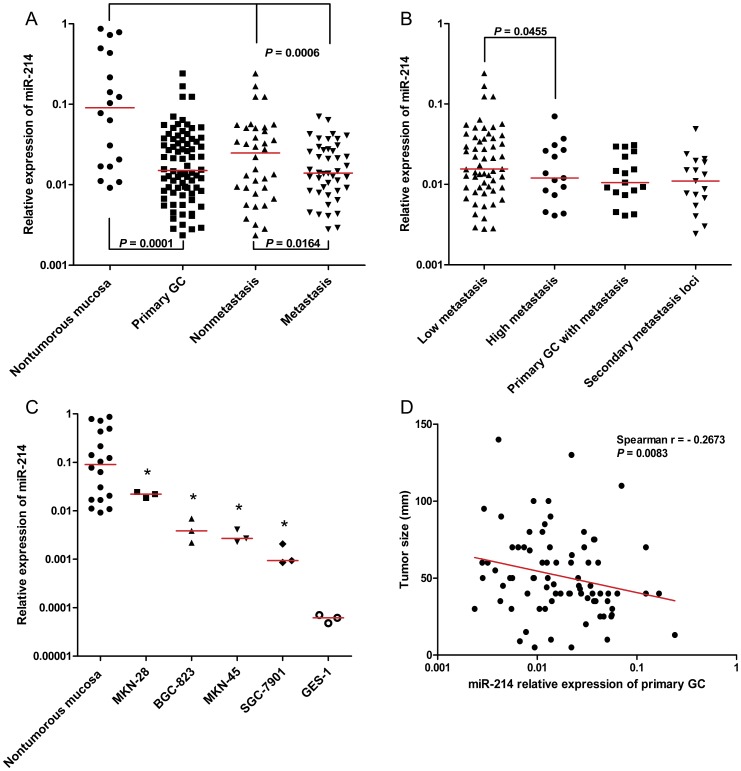
Figure 1. Expression of miR-214 in different samples and its association with tumour size.
(A) In comparison with 18 nontumourous gastric mucosa, miR-214 was significantly downregulated in 80 primary gastric tissues (P = 0.0001). MiR-214 expression was e en lower in primary gastric tissues with metastasis (Metastasis) than primary gastric tissues without metastasis (Nonmetastais). (B) Primary gastric tissues were further divided into a low-metastasis group and a high-metastasis group according to the number of lymph node metastasis. (The cutoff was set as six, which is a threshold to distinguish N0∼N1 and N2∼N3 in TNM stage (UICC, 2002). MiR-214 was dramatically reduced in high-metastasis group compared to low-metastasis group (P = 0.0455). (C) MiR-214 downregulation was validated in four gastric cell lines. Compared to well-moderately differentiated cell line MKN28, miR-214 was markedly attenuated in poorly differentiated cell line MKN45 and BGC823, and moderately-poorly differentiated and highly metastatic cell line SGC7901. However, we detected lower expression of miR-214 in GES-1, an immortalized gastric epithelial cell line, compared with four gastric cancer cells (* P<0.05). (D) Association between miR-214 expression and tumour size in primary GC was calculated by Spearman's correlation. Our data suggested that miR-214 expression was inversely correlated with tumor size (Spearman r = −0.2673, P = 0.0083).