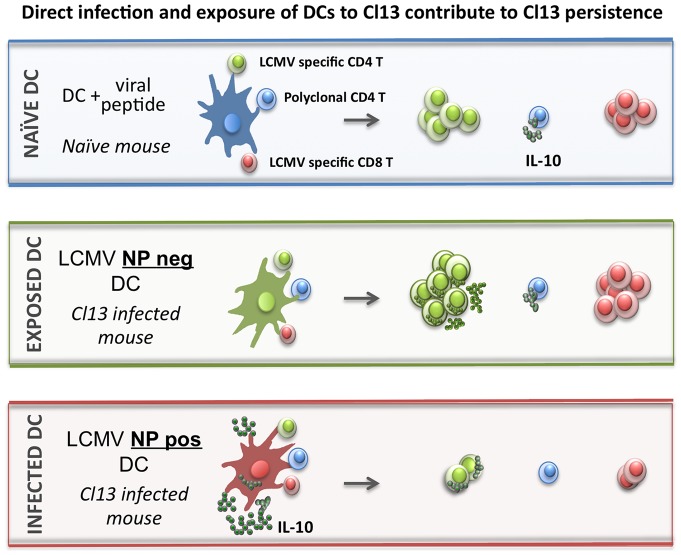
Figure 7. Direct infection and exposure of CD8αneg DCs to LCMV Cl13 differentially contribute to Cl13 persistence.
Naïve DCs, those harvested from uninfected mice, incubated with viral peptide are able to stimulate both LCMV specific CD4 and CD8 T cell proliferation, as well as induce IL-10 expression in naïve polyclonal CD4 T cells. Virally exposed DCs, those isolated from LCMV Cl13 infected mice and negative for surface expression of viral NP, are able to stimulate both LCMV specific CD4 and CD8T cell proliferation and also induce IL-10 expression in naïve polyclonal CD4 T cells. Smarta CD4 T cells cultured with Cl13 exposed DCs produce copious amounts of IL-10. Cl13 infected DC, positive for surface expression of viral NP, express enhanced levels of IL-10 as compared to either naïve or exposed DC, are unable to stimulate LCMV specific CD4 or CD8 T cells. The few CD4 T that are induced to proliferate in the presence of infected DCs express elevated levels of IL-10 as compared to either those cultured alone or in the presence of naïve DCs and LCMV peptide.