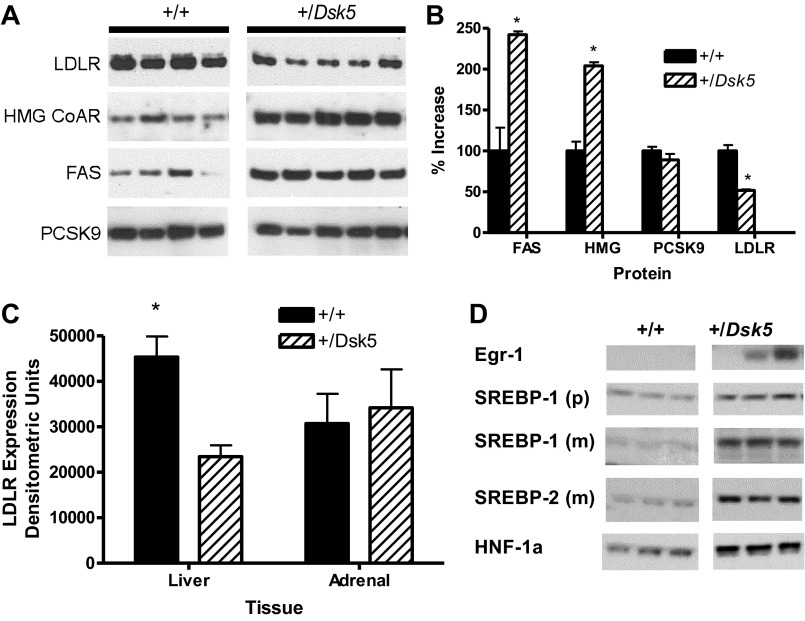
Fig. 7.
Adult male +/Dsk5 mice show decreased hepatic LDLR expression and increased hepatic 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl (HMG) CoA reductase and fatty acid synthase (FAS) expression. A: an immunoblot analysis was carried out for 4 proteins that play a role in the lipid profile of the liver, including LDLR, HMG CoA reductase, FAS, and PCSK9. Each lane includes protein from the liver of a single animal. B: we quantified the results obtained in the immunoblot from A and found a significant increase in expression for FAS and HMG CoA reductase, as well as a significant decrease for the LDLR in the +/Dsk5 mice compared with the +/+ littermates. No differences were observed for PCSK9 *P < 0.05. C: we analyzed by immunoblot the expression of LDLR in several different tissues. The signal intensity for LDLR expression was comparable in the liver and adrenal gland. There is a significant difference (*P < 0.015) in LDLR expression between the +/+ and +/Dsk5 liver but not for the adrenal. D: we evaluated the hepatic expression levels of several transcription factors by immunoblot that regulate cholesterol and fatty acid levels including early growth response-1 (Egr-1), sterol-regulatory element-binding protein (SREBP)-1, SREBP-2, and hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF)-1α. The antibodies used recognize the SREBP1 precursor (p) as well as the smaller, cleaved “mature” form (m) but only the mature SREBP2 form (m). The expression levels were increased by several times for each protein in the +/Dsk5 compared with +/+, with P < 0.05 or lower.