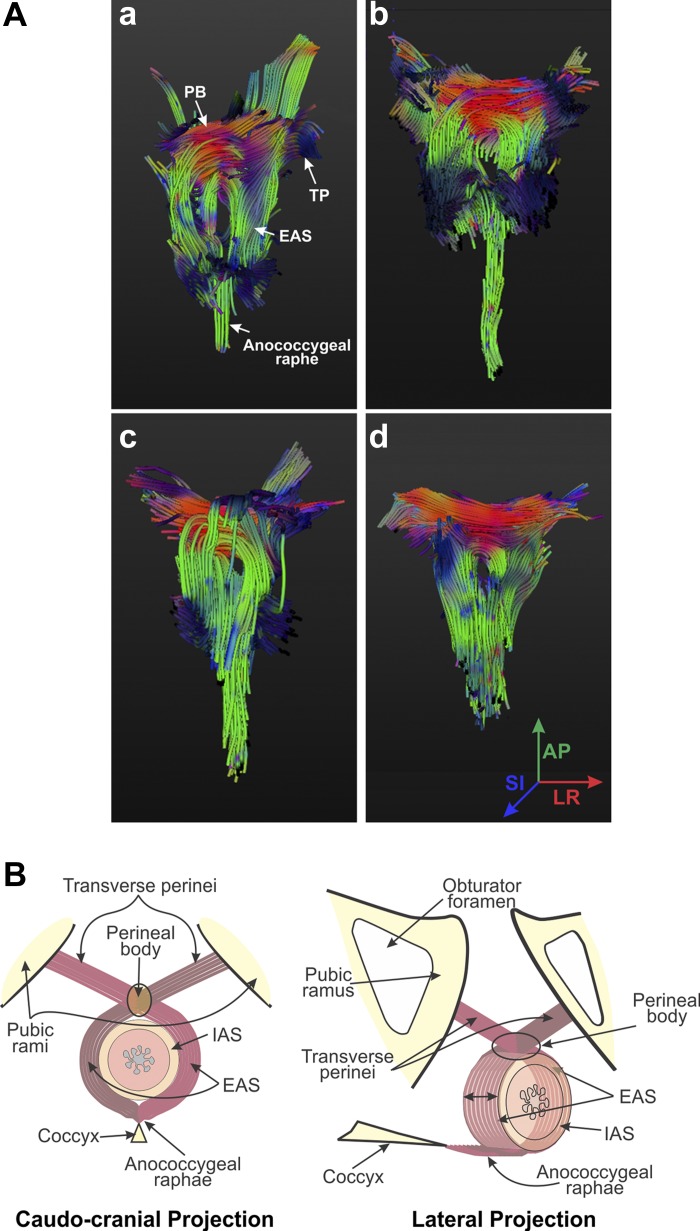
Fig. 4.
A: fiber tracking of the EAS muscle complex. Fiber tracking, utilizing the tensor images in Fig. 3, illustrates results obtained in 4 different subjects (a–d). Colors of the fibers at different points are indicative of their directions, as shown in d. As shown in a–d, EAS muscle fibers cross over from one side to the other in the PB to continue as the TP/BS muscles. Dorsally and caudally, muscle fibers continue as the anococcygeal raphe. Regions of the IAS and anal canal are depicted as a signal void in a–d. B: schematic of the EAS muscle complex. On the basis of US images, PD MRIs, DT images, and magnetic resonance fiber tracking, we propose “purse-string” morphology of the EAS complex.