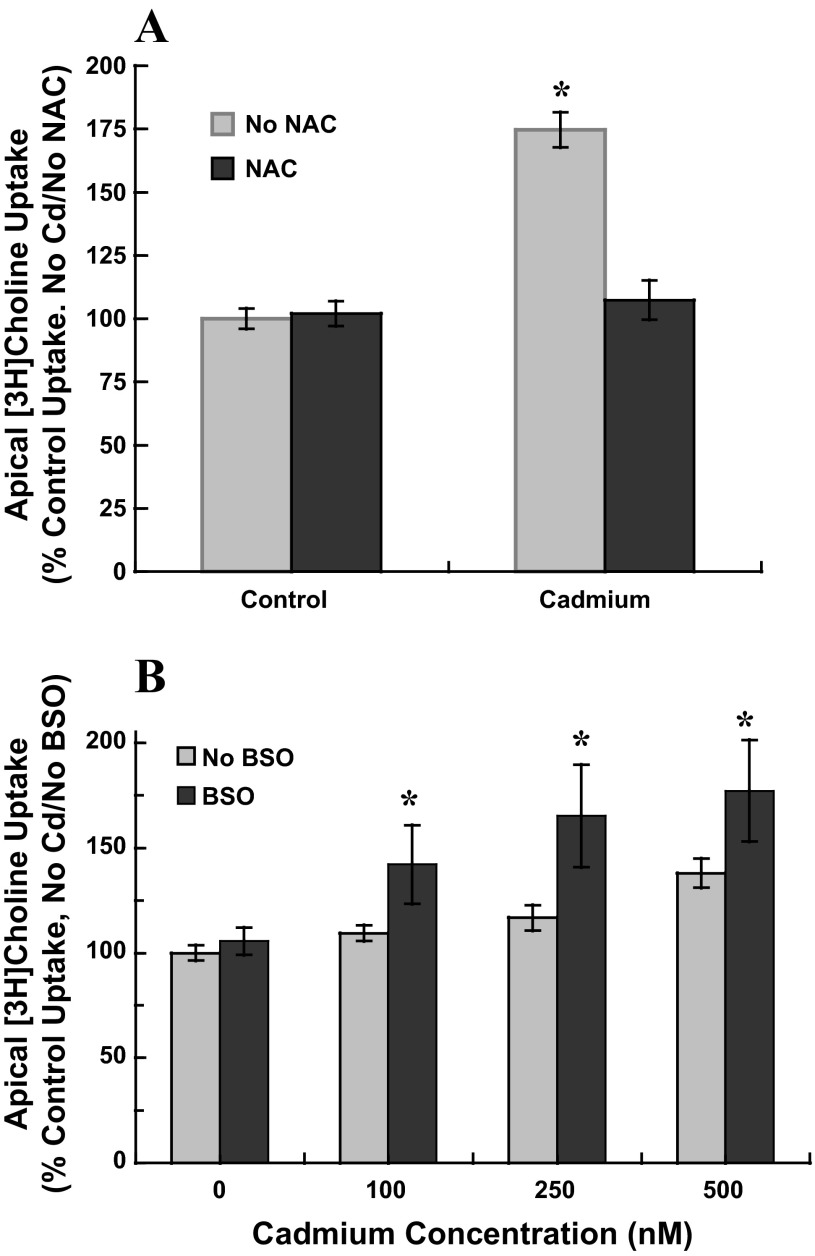
Fig. 3.
Apical uptake of [3H]choline in cadmium-exposed cultured choroid plexus epithelial cells treated with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) or l-buthionine sulfoximine (BSO). A: confluent monolayers grown on impermeable supports were pretreated in serum-free for 12 h with 1 mM NAC before 12-h exposure to 0 or 500 nM CdCl2 with 1 mM NAC; in parallel, representative cells were pretreated in serum-free medium for 12 h without NAC before 12-h exposure to 0 or 500 nM CdCl2. B: cells were pretreated in serum-free for 12 h with 100 μM BSO before 12-h exposure to 0, 250 or 500 nM CdCl2 and 100 μM BSO; in parallel, representative cells were pretreated in serum-free medium for 12 h without BSO before 12-h exposure to 0, 250, or 500 nM CdCl2 without BSO. A and B: after treatment, cells were rinsed and incubated (30 min, 37°C) in artificial CSF (10 mM Tris·HEPES, pH 7.4) with 10 μM [3H]choline chloride ± 750 μM hemicholinium-3; transport buffer did not contain cadmium, NAC or BSO. [3H]Choline uptake was expressed as the percentage of mediated uptake in nontreated control cells, i.e., 24 h in serum-free medium without cadmium, NAC, or BSO. Values are expressed as means ± SE; effects of NAC and BSO were each tested in three separate culture preparations (n = 3). *Significantly different than nontreated controls (No Cd/No NAC/No BSO); P < 0.05.