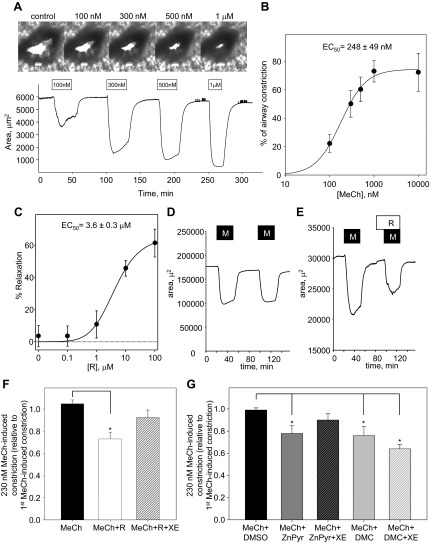
Fig. 4.
Attenuation of MeCh-induced airway constriction by KCNQ potassium channel activators. A, top: representative images of a small airway before treatment (control) and in the presence of MeCh at increasing concentrations (100 nM, 300 nM, 500 nM, 1 μM); bottom: corresponding representative time course of changes in the lumenal area of the same small airway. MeCh, at each concentration (as indicated by the open bars), was applied for 30 min (1 μM MeCh was applied for 20 min), followed by a 45-min washout in each case. B: concentration dependence of airway constriction in response to MeCh fitted to the Hill equation (n = 5). C: mean dose-response curve for retigabine (R)-induced relaxation of rat airways preconstricted with 230 nM MeCh fitted to the Hill equation (n = 6). MeCh was applied to each slice for 30 min before addition of retigabine for 30 min in the continued presence of 230 nM MeCh. A single concentration of retigabine was used for each precision-cut lung slice (PCLS; 6 slices total from 4 different animals for each concentration). D: representative time course of changes in the lumenal area of a small airway on repetitive application of 230 nM MeCh (M; 30 min), with 45 min washout between applications. E: representative time course of changes in the lumenal area of a small airway on application of 230 nM MeCh, followed by a 30-min washout, 15-min application of retigabine (R; 10 μM) alone, and then a second application of 230 nM MeCh for 30 min in the presence of retigabine (10 μM). F: summarized bar graph of 2nd MeCh-induced constriction, relative to 1st MeCh-induced constriction, when MeCh was applied alone (black bar, n = 5), in the presence of retigabine (10 μM, white bar, n = 8), and in the presence of retigabine (10 μM) together with XE991 (XE; 10 μM, striped bar, n = 7). *Significant difference from MeCh alone (ANOVA on ranks, P < 0.01). G: summarized bar graph of 2nd MeCh-induced constriction relative to 1st MeCh-induced constriction when MeCh (230 nM) was applied in the presence of vehicle (0.1% of DMSO, black bar, n = 5), in the presence of ZnPyr (1 μM, dark-gray bar, n = 6), in the presence of ZnPyr (1 μM) together with XE991 (10 μM, dark-gray striped bar, n = 5), in the presence of DMC (10 μM, light-gray bar, n = 6), and in the presence of DMC (10 μM) together with XE991 (10 μM, light-gray striped bar, n = 5). *Significant difference from MeCh applied in the presence of DMSO (one-way ANOVA, P < 0.05).