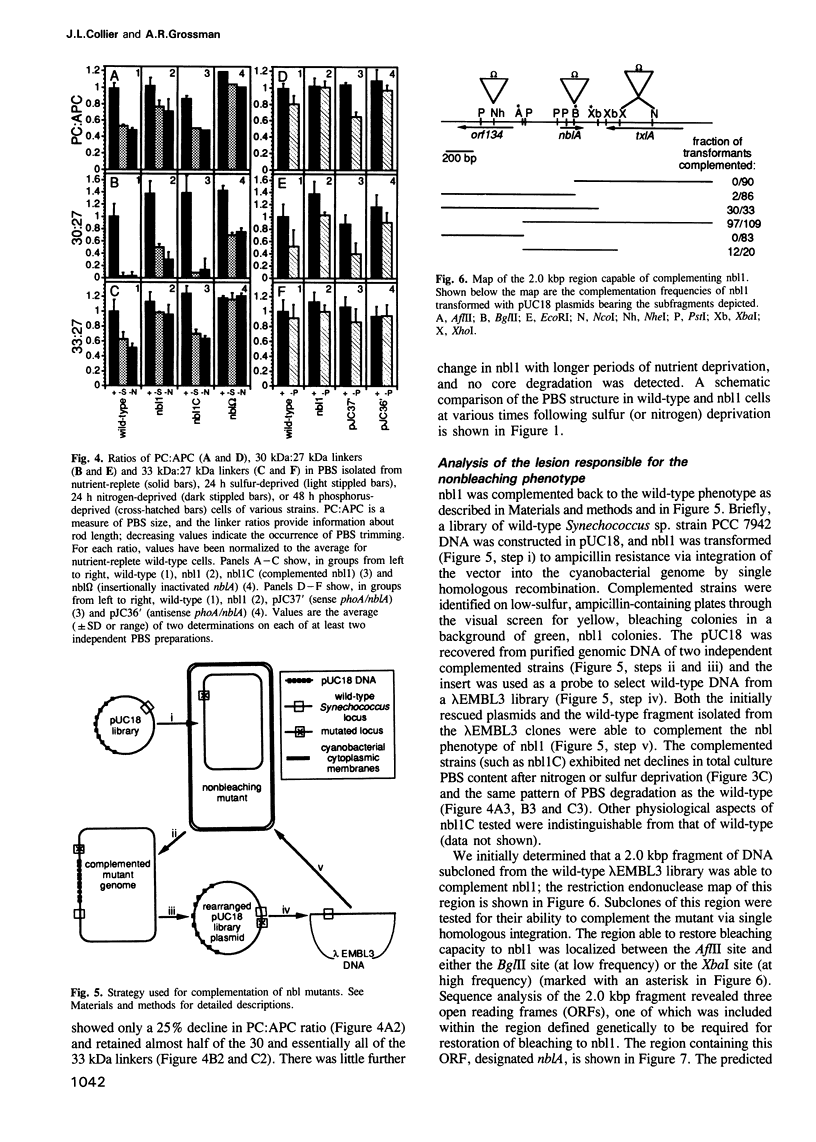
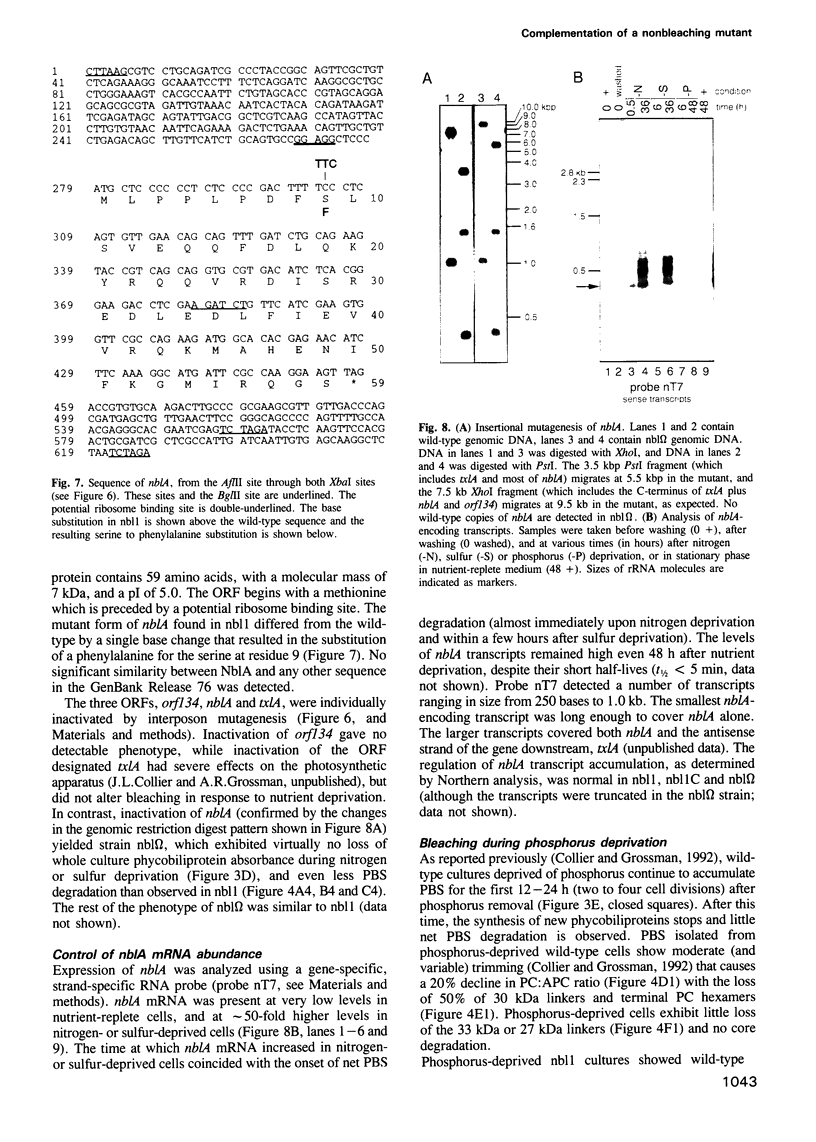
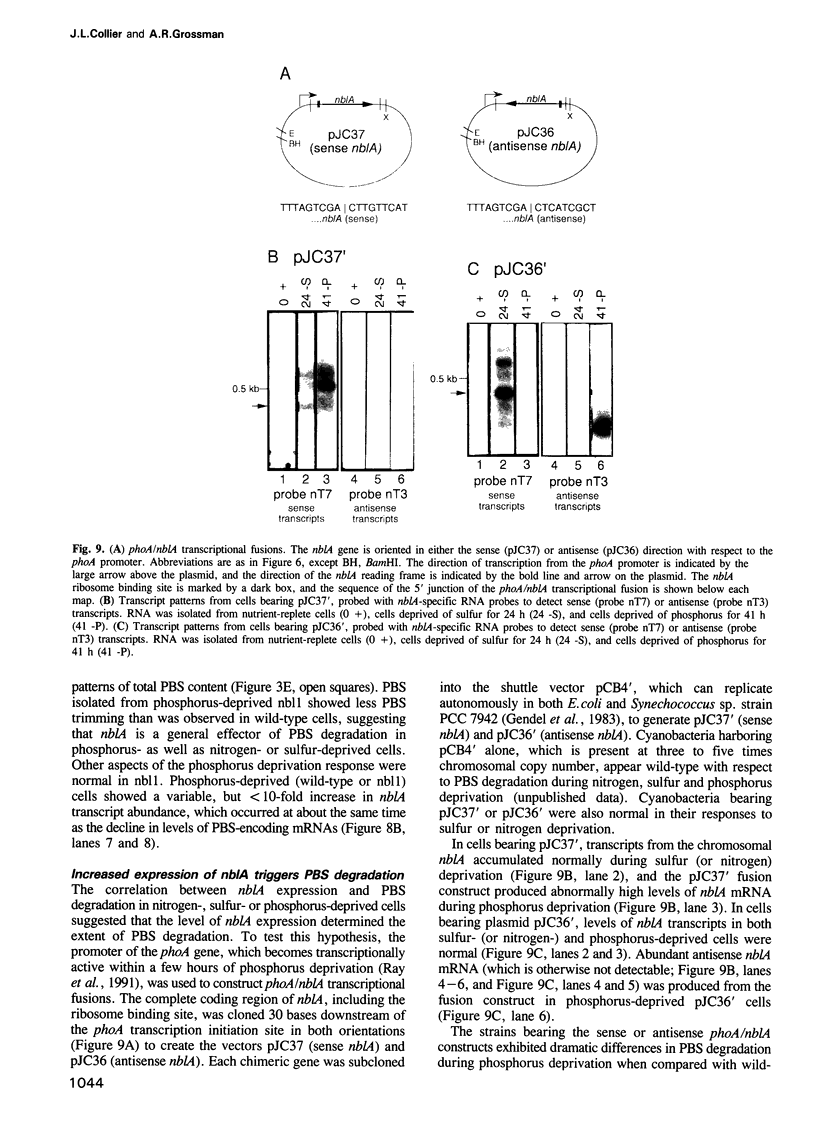
Abstract
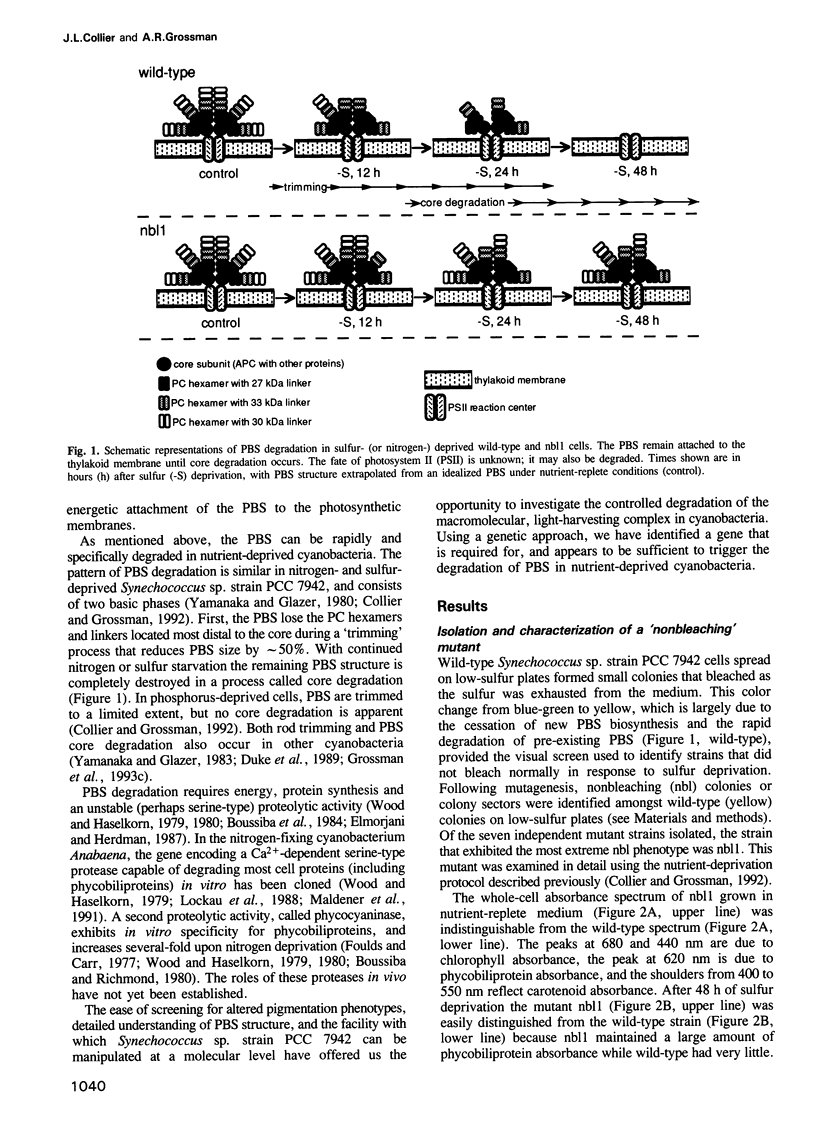
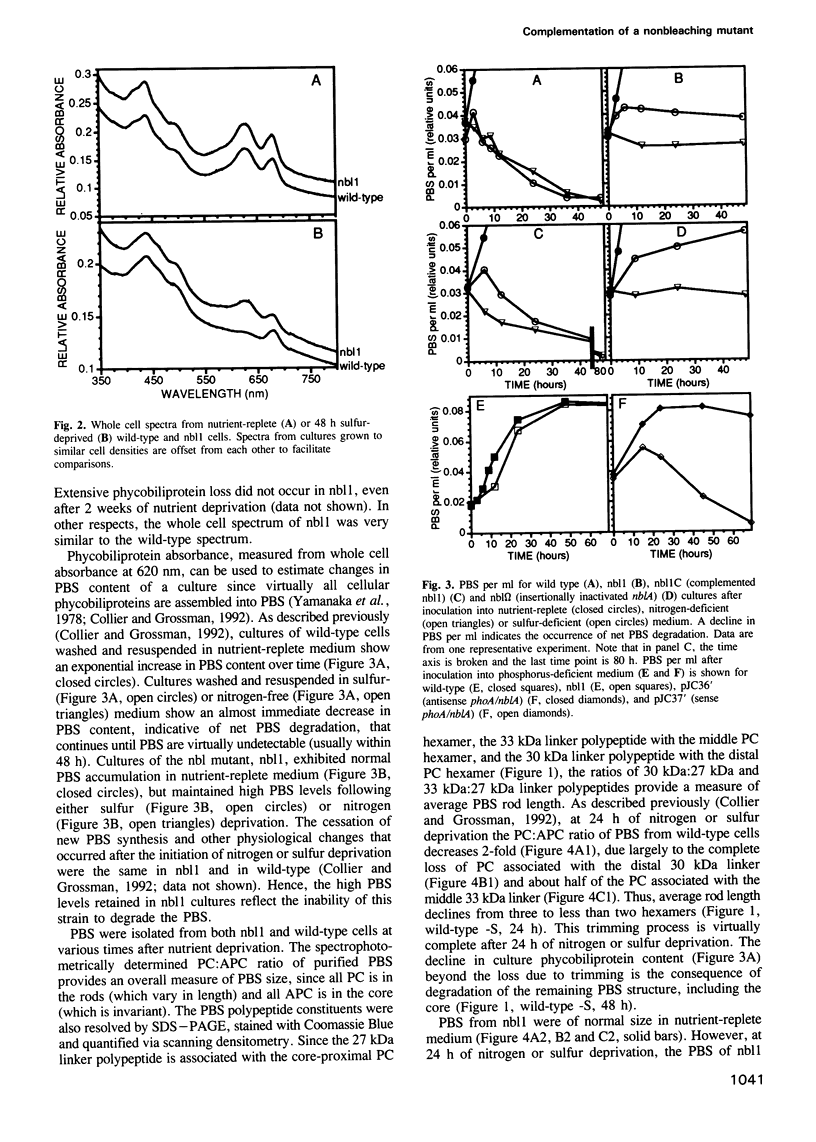
Phycobilisomes are the multiprotein complexes predominantly responsible for harvesting light energy in cyanobacteria and some eukaryotic algae. When the cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942 is deprived of an essential nutrient, the phycobilisomes are specifically and rapidly degraded. Degradation may be either partial (after phosphorus deprivation) or complete (after sulfur or nitrogen deprivation). We have developed a visual screen to obtain mutants unable to degrade their phycobilisomes upon nutrient starvation. Complementation of one of these mutants led to the identification of a gene, designated nblA, that encodes a 59 amino acid polypeptide essential for phycobilisome degradation. Transcription of nblA increases dramatically in sulfur- or nitrogen-deprived cells and moderately in phosphorus-deprived cells. Using the phosphorus-regulated alkaline phosphatase (phoA) promoter as a tool, we engineered constructs from which we could control the expression of either sense or antisense nblA. Increased expression of sense nbLA caused complete phycobilisome degradation during phosphorus deprivation, while expression of antisense nblA prevented phycobilisome degradation. Hence, nblA is necessary, and may be sufficient, for the degradation of phycobilisomes under adverse environmental conditions. Further investigation of the mechanism by which nblA causes phycobilisome destruction may reveal general principles that govern the specificity of macromolecular complex degradation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A., Bogorad L. Complementary chromatic adaptation in a filamentous blue-green alga. J Cell Biol. 1973 Aug;58(2):419–435. doi: 10.1083/jcb.58.2.419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collier J. L., Grossman A. R. Chlorosis induced by nutrient deprivation in Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942: not all bleaching is the same. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(14):4718–4726. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.14.4718-4726.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke C. S., Allen M. M. Effect of Nitrogen Starvation on Polypeptide Composition, Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase, and Thylakoid Carotenoprotein Content of Synechocystis sp. Strain PCC6308. Plant Physiol. 1990 Oct;94(2):752–759. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke C. S., Cezeaux A., Allen M. M. Changes in polypeptide composition of Synechocystis sp. strain 6308 phycobilisomes induced by nitrogen starvation. J Bacteriol. 1989 Apr;171(4):1960–1966. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.4.1960-1966.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gendel S., Straus N., Pulleyblank D., Williams J. Shuttle cloning vectors for the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1983 Oct;156(1):148–154. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.1.148-154.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N., Lundell D. J., Yamanaka G., Williams R. C. The structure of a "simple" phycobilisome. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Jul-Aug;134B(1):159–180. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(83)80103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Maurizi M. R. Regulation by proteolysis: energy-dependent proteases and their targets. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Dec;56(4):592–621. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.4.592-621.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. S., Grossman A. R. Changes in sulfate transport characteristics and protein composition of Anacystis nidulans R2 during sulfur deprivation. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):583–587. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.583-587.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. R., Schaefer M. R., Chiang G. G., Collier J. L. Environmental effects on the light-harvesting complex of cyanobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1993 Feb;175(3):575–582. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.3.575-582.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. R., Schaefer M. R., Chiang G. G., Collier J. L. The phycobilisome, a light-harvesting complex responsive to environmental conditions. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Sep;57(3):725–749. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.3.725-749.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. Mechanisms of intracellular protein breakdown. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:335–364. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.002003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. P., Johnston N. L., Cohen R. E. Crystal structure of a ubiquitin-dependent degradation substrate: a three-disulfide form of lysozyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4136–4140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau R. H., MacKenzie M. M., Doolittle W. F. Phycocyanin synthesis and degradation in the blue-green bacterium Anacystis nidulans. J Bacteriol. 1977 Dec;132(3):771–778. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.3.771-778.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudenbach D. E., Ehrhardt D., Green L., Grossman A. Isolation and characterization of a sulfur-regulated gene encoding a periplasmically localized protein with sequence similarity to rhodanese. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2751–2760. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2751-2760.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudenbach D. E., Grossman A. R. Characterization and mutagenesis of sulfur-regulated genes in a cyanobacterium: evidence for function in sulfate transport. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(9):2739–2750. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.9.2739-2750.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockau W., Massalsky B., Dirmeier A. Purification and partial characterization of a calcium-stimulated protease from the cyanobacterium, Anabaena variabilis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 1;172(2):433–438. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13906.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maldener I., Lockau W., Cai Y. P., Wolk C. P. Calcium-dependent protease of the cyanobacterium Anabaena: molecular cloning and expression of the gene in Escherichia coli, sequencing and site-directed mutagenesis. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jan;225(1):113–120. doi: 10.1007/BF00282649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matin A., Auger E. A., Blum P. H., Schultz J. E. Genetic basis of starvation survival in nondifferentiating bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:293–316. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurizi M. R. Proteases and protein degradation in Escherichia coli. Experientia. 1992 Feb 15;48(2):178–201. doi: 10.1007/BF01923511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed A., Jansson C. Influence of light on accumulation of photosynthesis-specific transcripts in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Dec;13(6):693–700. doi: 10.1007/BF00016024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami Y., Matsufuji S., Kameji T., Hayashi S., Igarashi K., Tamura T., Tanaka K., Ichihara A. Ornithine decarboxylase is degraded by the 26S proteasome without ubiquitination. Nature. 1992 Dec 10;360(6404):597–599. doi: 10.1038/360597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray J. M., Bhaya D., Block M. A., Grossman A. R. Isolation, transcription, and inactivation of the gene for an atypical alkaline phosphatase of Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7942. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4297–4309. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4297-4309.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M., Hoffman L., Dubiel W. The multicatalytic and 26 S proteases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6065–6068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer T., Seufert W. Genetic analysis of ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation. Experientia. 1992 Feb 15;48(2):172–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01923510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobias J. W., Shrader T. E., Rocap G., Varshavsky A. The N-end rule in bacteria. Science. 1991 Nov 29;254(5036):1374–1377. doi: 10.1126/science.1962196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. The N-end rule. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):725–735. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90285-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood N. B., Haselkorn R. Control of phycobiliprotein proteolysis and heterocyst differentiation in Anabaena. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1375–1385. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1375-1385.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanaka G., Glazer A. N., Williams R. C. Cyanobacterial phycobilisomes. Characterization of the phycobilisomes of Synechococcus sp. 6301. J Biol Chem. 1978 Nov 25;253(22):8303–8310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]