Figure 4. Tumor Targeting, antibody production, and induction of apoptosis in vivo.
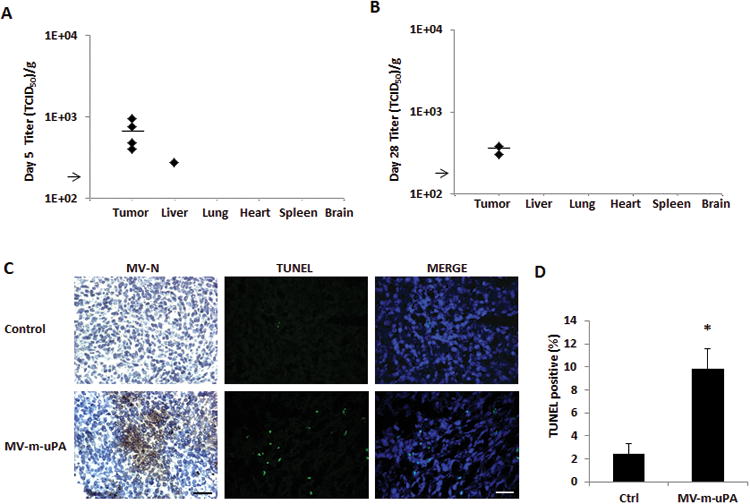
(A, B) Recovery of viable viral particles from tumor, liver, lung, heart, spleen and brain from mice at day 5 (A) and Day 28 (B) after virus treatment (n=5 mice per group). Tissues were processed and assays were preformed as in methods. Viral titers are displayed as TCID50/gram of tissue . Arrow represents the assay's limit of detection-LOD (1.26×102 TCID50/gram of tissue). (C) Immunocompetent (Balb/c) mice (n = 3 per group) bearing 4T1 tumors received two intravenous injections of either PBS or MV-m-uPA (1.5×106 TCID50). Tumors were harvested 3 days later and frozen tumor sections were used for immunostaining for measles N protein. Viral protein was detected in tumors after intravenous administration of the virus. TUNEL assay of tumors from mice treated with MV-m-uPA or PBS was performed as in materials and methods (n=3 per group). Scale bar = 200 μm. (D) Quantitative analysis of TUNEL–positive nuclei in 4 microscopic fields per section per sample (displayed as percentage of positive/total nuclei; n = 3 per group). *, P < 0.01, MV-m-uPA versus ctrl.
