Fig. 1.
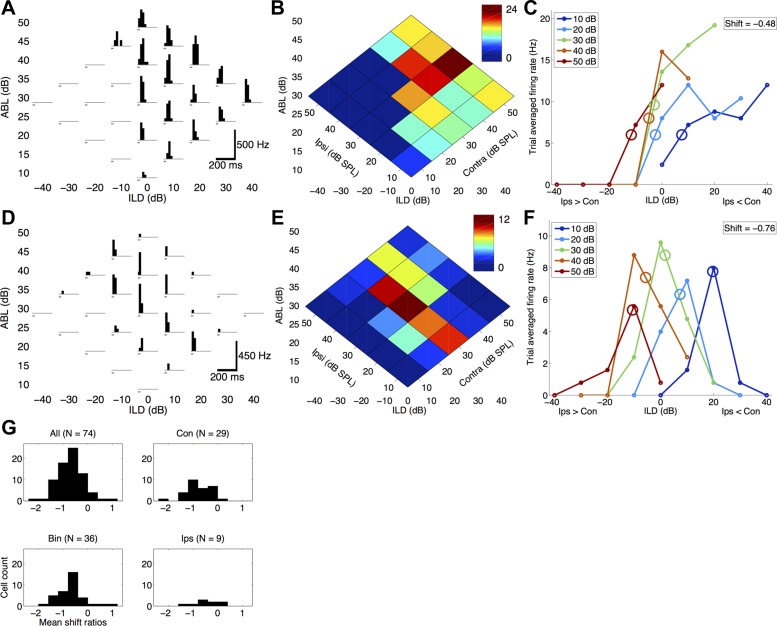
Spiking interaural level difference (ILD) responses in the rat auditory cortex shift toward the ipsilateral ear (negative shifts) with increasing ipsilateral sound level. A–F: 2 representative examples showing negative ILD response shifts in both contralateral-preferring (A–C; cell 120810-MK-3-2) and binaural-preferring (D–F; cell 091410-WS-2-1) cells. A and D: spiking responses to the binaural stimulus array. Each histogram shows the firing rate in 20-ms bins (accumulated from 10 trials). White noise bursts (25-ms duration) are indicated in gray. B and E: trial-averaged normalized firing rate heat maps of the same data shown in A and D. Dark red indicates maximum firing rate, and dark blue indicates minimum firing rate. Each binaural stimulus can be represented either as an ILD-average binaural level (ABL) combination (x- and y-axes) or as a contralateral and ipsilateral sound level (diagonal axes). For example, the green response at ILD 20, ABL 20 corresponds to Contra 30, Ipsi 10. C and F: firing rate ILD response curves. Ipsilateral level is held constant for each curve (see inset for color code) as a function of ILD. In other words, each line is a diagonal slice through B, parallel to the Contra axis. C: contralateral-preferring cell with a mean ILD response shift of −0.48 dB/dB (SD = 0.44; see methods for detailed description). Circles denote half-maximal ILD values. Negative ILDs correspond to greater ipsilateral level (Ips > Con); positive ILDs correspond to greater contralateral level (Ips < Con). F: binaural-preferring cell with a mean ILD response shift of −0.76 dB/dB (SD = 0.33). Circles denote the average of left and right half-maximal ILD values; thus the circles are found near the maxima. G: population histograms showing that the majority of cells (89.2%) have negative response shifts (top left, 66/74 cells), regardless of binaural preference categorization (Con, contralateral preferring; Bin, binaural preferring; Ips, ipsilateral preferring).