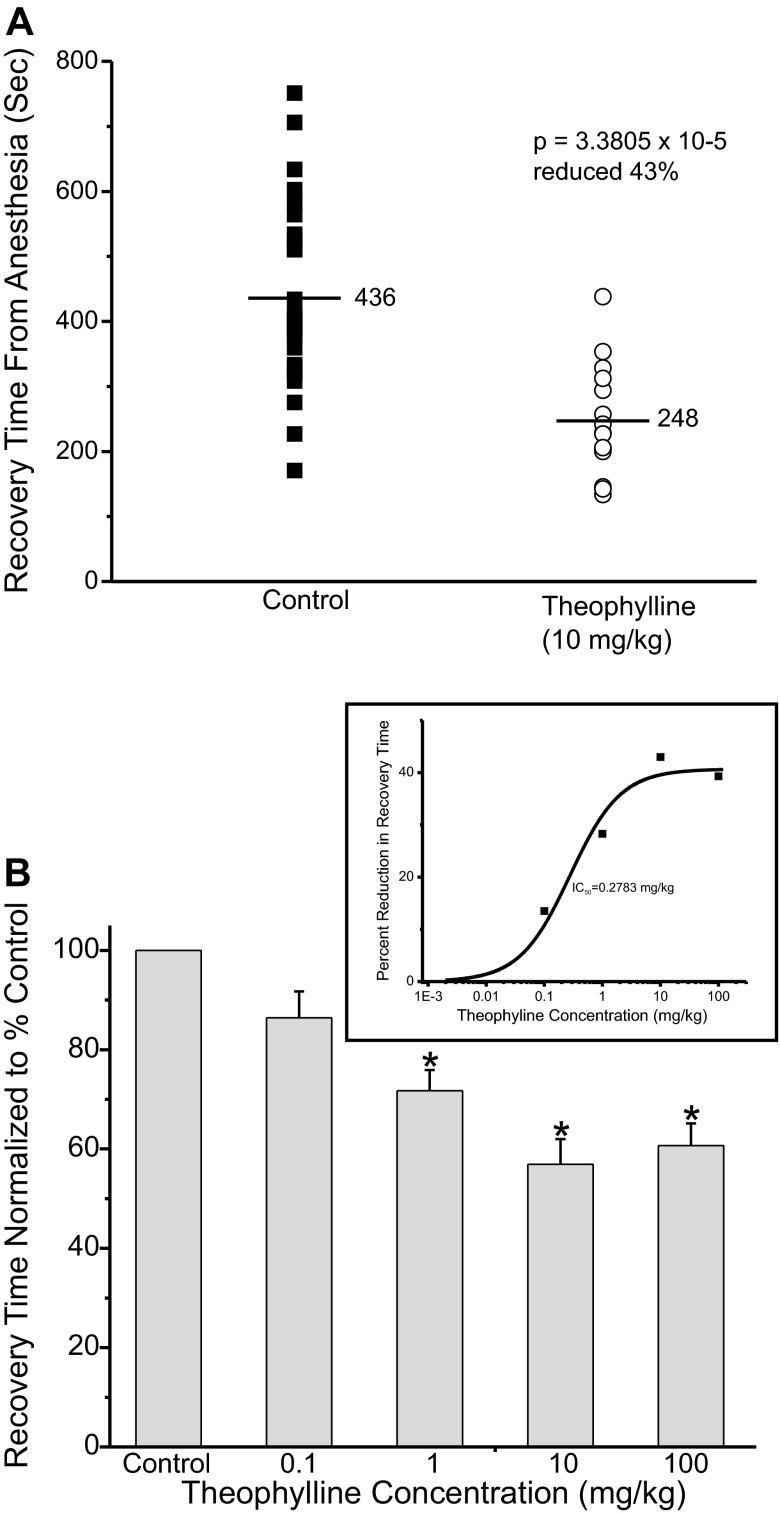
Fig. 5.
Theophylline accelerated recovery from isoflurane anesthesia. A: adult rats were anesthetized as described in Fig. 3. Thirty minutes before discontinuing the anesthetic the animals received an intravenous injection of either saline (control, ■) or saline with 10 mg/kg theophylline (○). The anesthetic was then terminated and the animals were allowed to recover. Each symbol represents a single trial of 1 rat. B: average waking time normalized to control value, set to 100%, at different theophylline concentrations. (n = 12; control, n = 21; 0.1 mg/kg, n = 11; 1 mg/kg, n = 15; 10 mg/kg, n = 12; 100 mg/kg). Inset: plots of percent reduction in waking time as a function of the theophylline concentration. The midpoint was ∼0.28 mg/kg forskolin, max reduction in recovery time ∼41%. *Waking times significantly different from control.