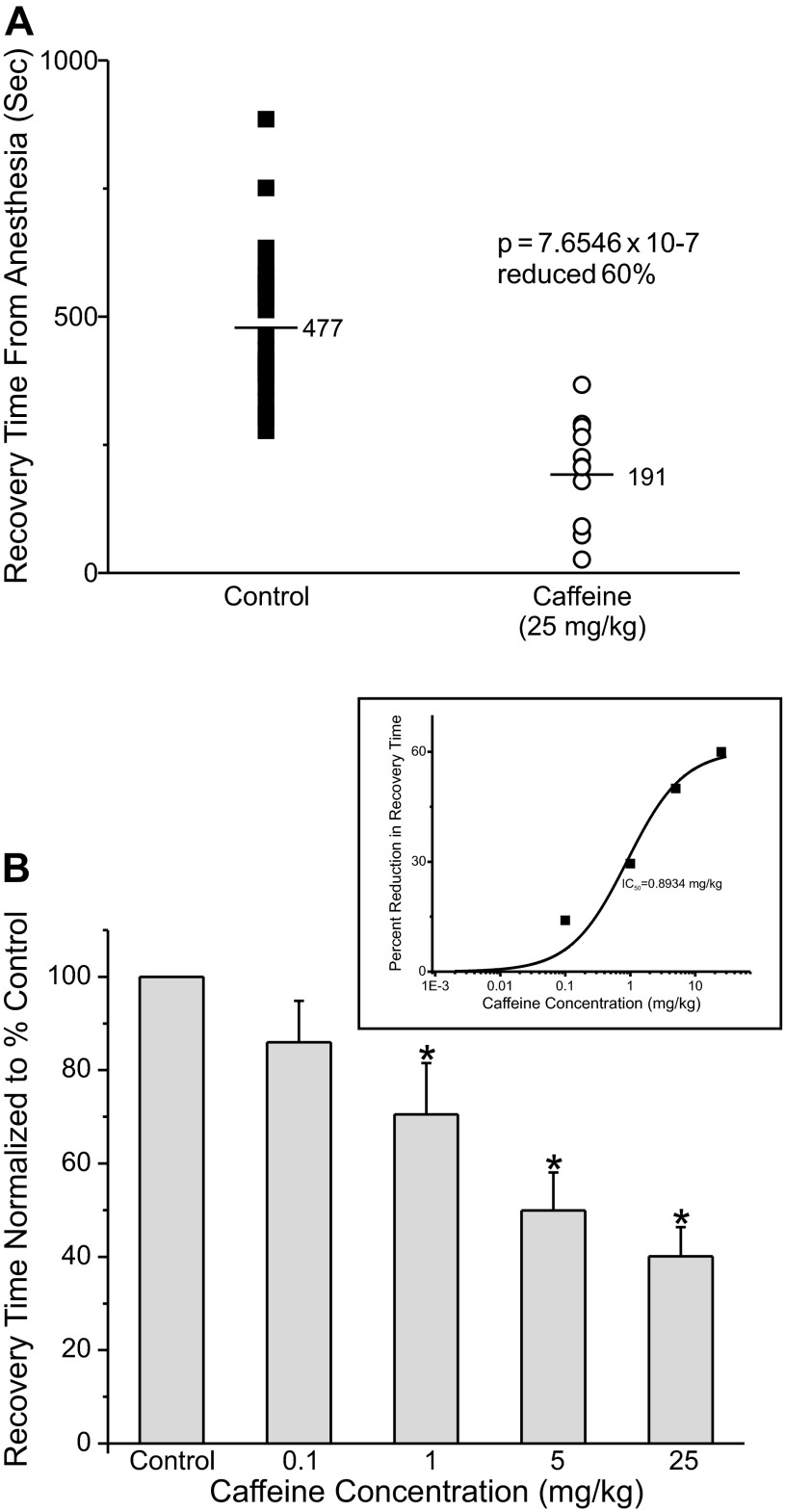
Fig. 6.
Caffeine accelerated recovery from isoflurane anesthesia. A: adult rats were anesthetized as described in Fig. 3. Five minutes before discontinuing the isoflurane the animals received an intravenous injection of either saline (control, ■) or saline with 25 mg/kg caffeine (○). The isoflurane was terminated and the animals were allowed to recover. B: average waking time normalized to the control value, set to 100%, at different caffeine concentrations (n = 13; control, n = 8; 0.1 mg/kg, n = 13; 1 mg/kg, n = 12; 5 mg/kg, n = 12; 25 mg/kg). Inset: plot of percent reduction in waking time as a function of the caffeine concentration. The midpoint was at ∼0.9 mg/kg caffeine and the maximal reduction of waking time was ∼60.5%. *Waking times significantly different from control.