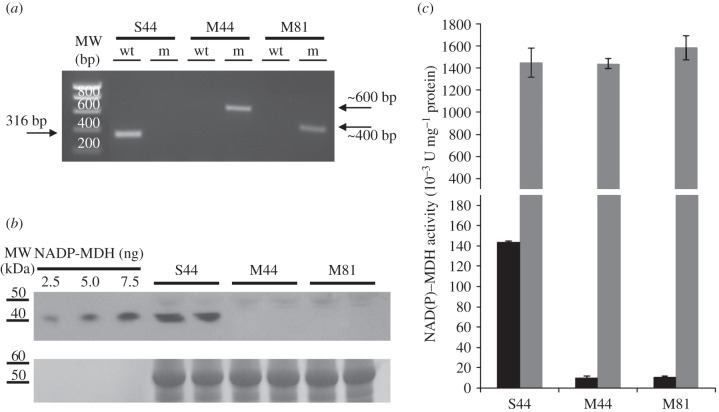
Figure 2.
Molecular characterization of the NADP–MDH knockout lines. (a) PCR screening with genomic DNA by amplification of either the T-DNA left border/nadp–mdh gene junction (m) or a wild-type nadp–mdh gene-specific fragment encompassing the site of T-DNA insertion (wt). Expected sizes (in base pairs, bp) of PCR products are shown as well as molecular weight (MW) markers. (b) Detection of NADP–MDH protein in wild-type (S44) and in mutant plants (M44 and S81). Western blot analysis of Arabidopsis leaf proteins along with varying amounts of sorghum NADP–MDH as control was made using antibodies raised against sorghum NADP–MDH. (c) NAD(P)–MDH leaf activity. Total leaf NADP–MDH capacity (black columns) was measured after a reducing (enzyme activation) treatment of soluble crude leaf extracts. For comparison, NAD–MDH activity (grey columns) was also measured.