Figure 1.
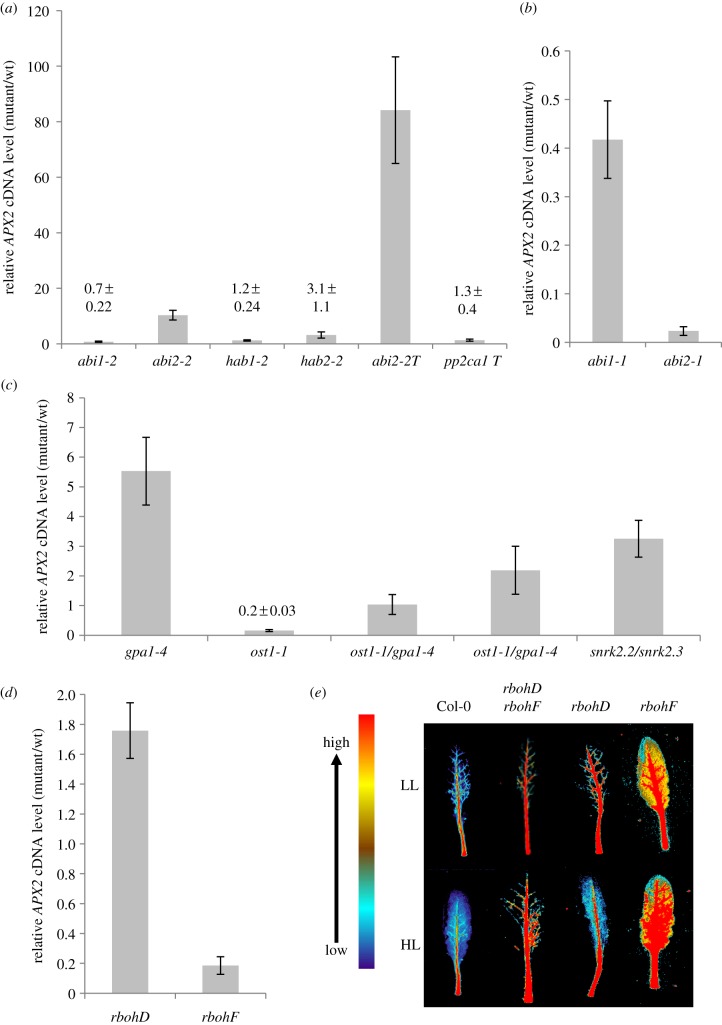
Expression of APX2 and ARU staining for extracellular H2O2 in Arabidopsis leaves subjected to HL. (a) APX2 cDNA levels from HL-exposed single and triple PP2C mutants compared with HL exposed Col-0. HL exposures (1500 µmol m−2 s−1 PPFD for 30 min) were conducted on 5-week-old short day-grown rosettes and RNA extracted from fully expanded leaves. cDNA levels were determined by qPCR using a SYBR Green-based assay (see Material and methods) with CYC as the reference gene. Values are means (±s.e.) of two experiments each with six plants used (n = 12). (b) Relative APX2 cDNA levels in abi1-1 and abi2-1. Experimental conditions were as in (a), except that these are data (means±s.e.) from one experiment of six plants (n = 6). (c) Relative APX2 cDNA levels in ost1-1/gpa1-4, ost1-1, gpa1-4 and snrk2.2/snrk2.3. The HL conditions, sample size and qPCR were as in (a). Two individual lines of the double mutant were analysed. Wild-type controls were Ler for ost1-1, Col-0 for gpa1-4 and snrk2.2/snrk2.3 and an F3 Ler/Col-0 hybrid (see Material and methods). (d) APX2 cDNA levels in rbohD and rbohF relative to Col-0. The HL conditions, sample size and qPCR were as in (a). (e) Resorufin fluorescence in HL-exposed detached leaves of rbohD, rbohF and rbohD/rbohF. ARU (40 µM) was infiltrated into leaves (see Material and methods) and false-coloured image produced digitally against a scale of the fluorescence emission. (Online version in colour.)