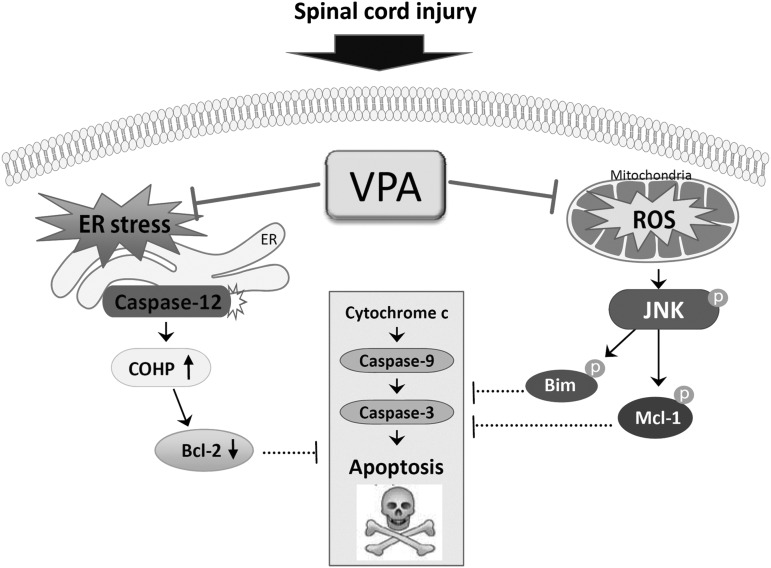
FIG. 9.
Schematic diagram showing the neuroprotective effect of valproic acid (VPA) after SCI. Both endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced caspase-12 activation and reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) activation contributed to ventral motor neuron death after SCI, which was inhibited by VPA.