Figure 2.
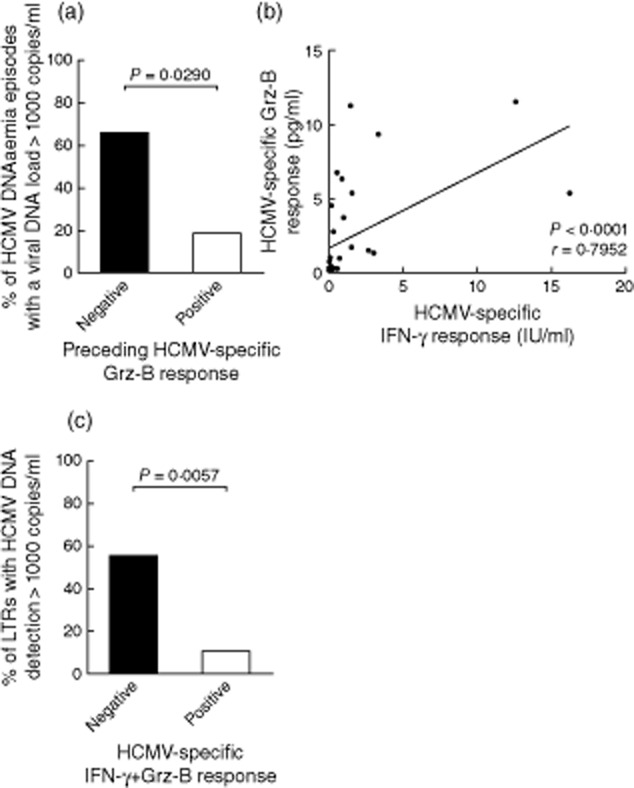
Statistical analysis of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV)-specific granzyme B (Grz-B) responses and HCMV DNAaemia. HCMV-specific Grz-B responses which were detected prior to the onset of HCMV DNAaemia differed in lung transplant recipients (LTRs) who subsequently developed DNAaemia episodes with high (> 1000 copies/ml) and low viral DNA loads. In 10 of 16 (62·5%) episodes that were preceded by a negative Grz-B response, viral DNA loads exceeded 1000 copies/ml, versus three of 16 (18·8%) episodes which were preceded by a positive Grz-B response (Fisher's exact test, P = 0·0290) (a). The levels of HCMV-specific Grz-B responses that were detected prior to the 32 HCMV DNAaemia episodes correlated with the detected levels of specific interferon (IFN)-γ (P < 0·0001, Spearman's rank test) (b). Simultaneous detection of specific Grz-B and IFN-γ responses affected the occurrence of high HCMV DNA loads (> 1000 copies/ml) during the subsequent follow-up. HCMV DNAaemia with viral DNA loads exceeding 1000 copies/ml developed in 11 of 20 (55%) LTRs who previously either showed a negative Grz-B or negative IFN-γ response, but occurred in only two of 19 (10·5%) LTRs who displayed a double-positive Grz-B and IFN-γ response (P = 0·0057, Fisher's exact test).
