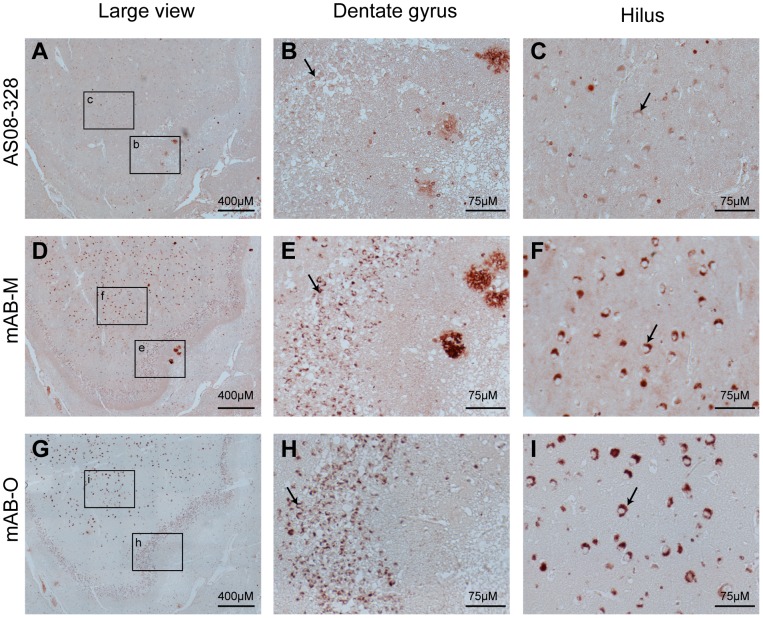
Figure 5. IHC of human hippocampus from an AD-affected individual.
IHC was used to illustrate binding specificity and structural preferences of mAB-O and mAB-M upon binding to ex vivo material. Hippocampus sections were from a post-mortem AD-affected human brain (A–C) The binding pattern from a polyclonal rabbit anti-Aβ antibody illustrating both plaques as well as an intracellular form of Aβ that is abundant in the hilar neurons. (D–F) The staining pattern of mAB-M in which Aβ plaques near the dentate gyrus (E) are readily stained. (G–I). The binding pattern of mAB-O illustrates an inability to stain Aβ plaques and indicates an alternative structural preference compared to mAB-M. A strong binding to the intracellular form of Aβ is observed in the hilus area. The granular cells of the dentate gyrus (B, E, and H) and the neurons of hilus (C, F, and I) are indicated with arrows and represent the highe magnification images of respective selected areas in A, D and G.