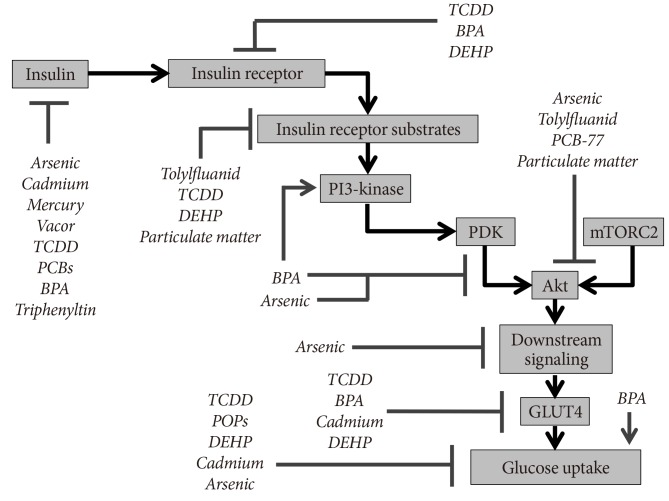
Fig. 1.
Insulin signaling targets of endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs). Multiple studies have examined the effects of EDCs on various aspects of insulin synthesis, release, and cellular action. The molecular targets identified from these various studies are summarized. Of note, this figure synthesizes data from various model systems, including multiple different targets of insulin action (i.e., adipose tissue, liver, and muscle). The data has been combined for clarity but should not be understood to mean that the EDCs shown exert similar effects in all biological tissues or in all species. TCDD, 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin; BPA, bisphenol A; DEHP, diethylhexylphthalate; PCB, polychlorinated biphenyl; PDK, phosphoinositide-dependent kinase; mTORC2, mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2; POP, persistent organic pollutant; GLUT4, glucose transporter 4.