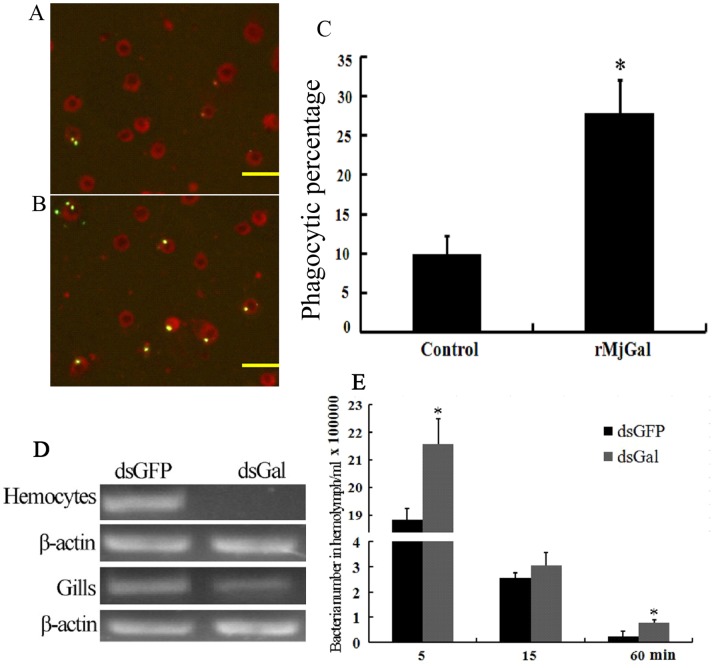
Figure 8. MjGal promoted bacterial clearance from hemolymph.
Bacteria phagocytosis assay: fluorescently labeled V. anguillarum (5×107 cells) were coated with either Trx-His (A, the control) or rMjGal (B) and injected into shrimp. The hemocytes were collected after 30 min and placed onto the glass slides. Subsequently, trypan blue solution (2 mg/ml PBS) (Amresco) was added to quench the fluorescence of non-phagocytosed bacteria. The phagocytosis by hemocytes was observed at 400× magnification, and phagocytosed bacteria counted at 200×magnification under the fluorescence microscope. (A) Hemocytes from shrimp injected with V. anguillarum coated with Trx-His. (B) Hemocytes from shrimp injected with V. anguillarum coated with rMjGal. (C) The phagocytic percentages of two groups (*P<0.05). Bar = 50 µm. (D) RNA interference assay: shrimp were injected with dsRNAs twice to silence MjGal expression, and or with GFP dsRNAs as control. Vibrio anguillarum (2×107 cells) were injected into shrimp after the second injection. Hemolymph was collected from the two groups at 5, 15, 60 min post-infection, and serially diluted with PBS. Fifty µl of each sample was plated onto 2216E agar plates and incubated at 37°C overnight. RNA was extracted from hemocytes and gills of two groups, and tested by RT-PCR to confirm silencing of MjGal expression. (E) The bacterial counts in hemolymph samples collected at 5, 15 and 60 min from shrimp from the dsMjGal and dsGFP groups.