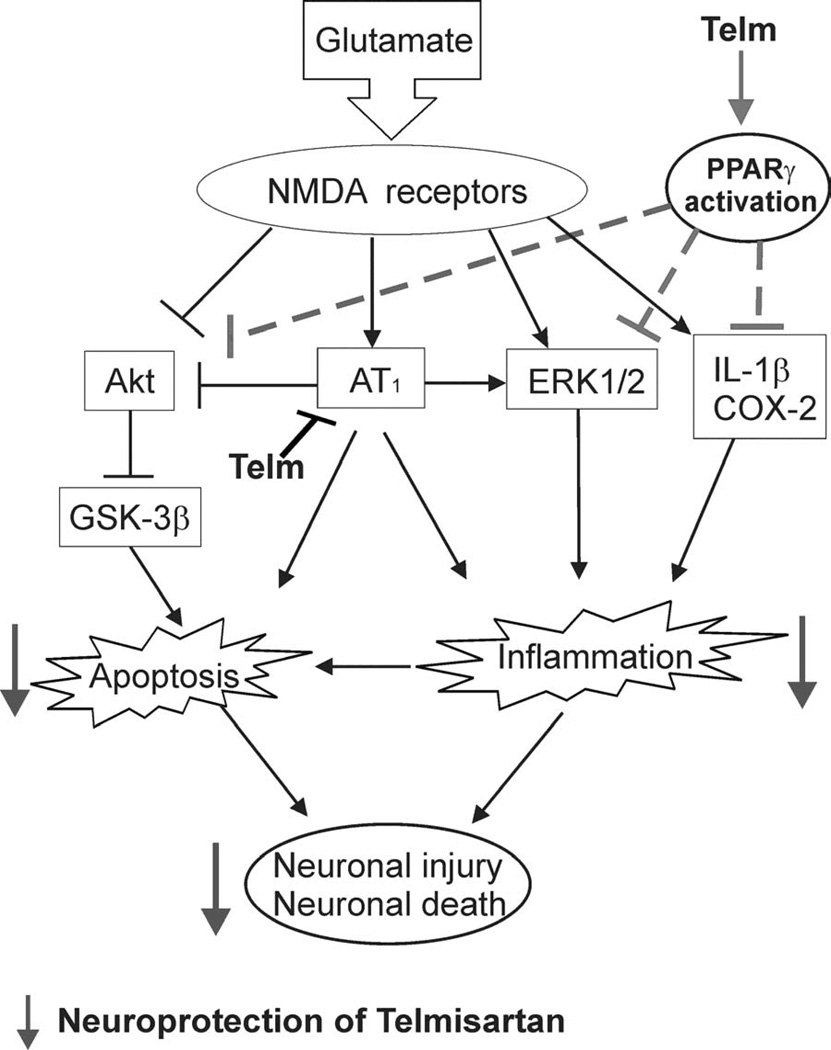
Fig. 11.
Proposed mechanisms of telmisartan neuroprotection. Glutamate stimulates NMDA receptors and induces neuronal injury by increasing apoptosis and inflammation. Mechanisms include increased AT1 receptor expression, inhibition of the anti-apoptotic Akt pathway, and ERK1/2 stimulation. Telmisartan reduces glutamate-induced apoptosis and inflammation in CGCs. Telmisartan neuroprotection is the result of dual AT1 receptor blockade and PPARγ activation, decreasing apoptosis and inflammation by mechanisms involving a reduction of glutamate-induced alterations in the Akt/GSK-3β and ERK1/2 pathways.