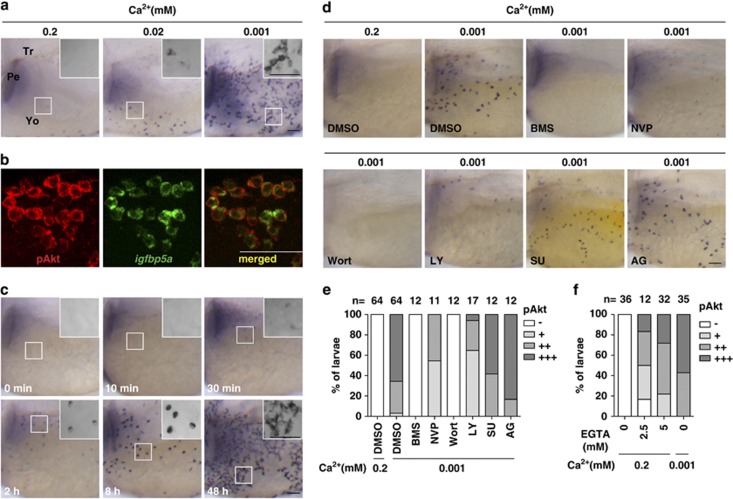
Figure 3.
Low [Ca2+] treatment results in a rapid and sustained activation of IGF-PI3K-Akt in NaR cells. (a) Low [Ca2+] treatment induces the activation of phospho-Akt (pAkt) in yolk sac cells. Larvae (72 hpf) were transferred to artificial freshwater with the indicated [Ca2+], raised to 120 hpf, and stained for pAkt. Inserts are higher magnification views. Tr, trunk; Pe, pectoral fin; Yo, yolk sac. Scale bar=50 μm. (b) All pAkt-positive cells are NaR cells. Larvae (72 hpf) were transferred to artificial freshwater containing 0.001 mM [Ca2+]. After 48 h, they were analyzed by in situ hybridization for igfbp5a mRNA and pAkt immunostaining. (c) Time course effect. Larvae (72 hpf) were transferred to artificial freshwater containing 0.001 mM [Ca2+], sampled at the time points indicated, and stained for pAkt. Inserts are higher magnification views. (d and e) The low [Ca2+]-induced pAkt activation is IGF1R- and PI3K-dependent. Larvae (72 hpf) were transferred to 0.001 mM [Ca2+] water containing DMSO, BMS-754807 (BMS, 0.3 μM), NVP-AEW541 (NVP, 6 μM), wortmannin (Wort, 0.06 μM), LY294002 (LY, 5 μM), SU5402 (SU, 15 μM), or AG1478 (AG, 4 μM). After 8 h, they were stained for pAkt. Representative views are shown in (d). The animals were scored according to the scoring system shown in Supplementary Figure S1a and the quantitative results from three independent experiments are shown in (e). The total number of fish analyzed is shown on the top of each column. (f) Effect of EGTA on pAkt. 72 hpf larvae were transferred to 0.2 mM [Ca2+] water containing the indicated concentrations of EGTA. After 8 h, they were stained for pAkt. The quantitative results are shown. Fish larvae raised in 0.001 mM [Ca2+] water were used as controls