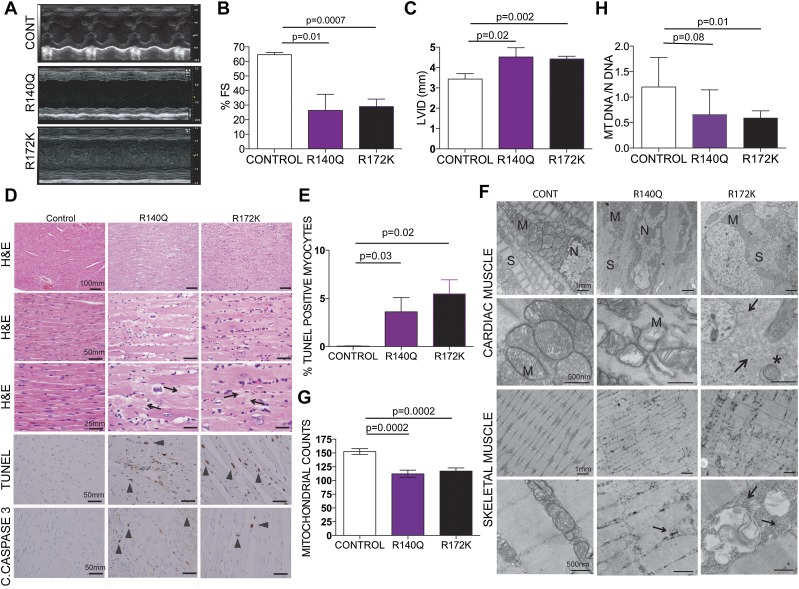
Figure 2.
Physiologic and structural defects in IDH mutant muscle. (A) Representative M mode images of the echocardiograms of the mice with the indicated genotypes. (B) Fractional shortening (%FS) measured from the M mode images of the echocardiograms plotted for each genotype (n = 3, 3, and 6 mice, respectively). (C) Left ventricular internal diameter in diastole (LVID) measured from the B mode images of the echocardiograms showing dilatation in the mutant IDH hearts (n = 3, 3, and 6, respectively). (D) Representative histology of the hearts from the indicated genotypes. H&E-stained longitudinal sections of IDH2 mutant cardiac muscle show myocyte hypertrophy characterized by fiber thickening and nuclear enlargement with increased pleomorphism. TUNEL staining and immunohistochemistry for cleaved caspase-3 on formalin-fixed tissues show increased apoptosis in the R140Q and R172K hearts compared with controls. Arrowheads point to fibrotic areas. Bars show the indicated lengths and are the same across the images on the same row. (E) Quantification of the TUNEL staining on the heart tissues (n = 3, 3, and 6, respectively). (F) Representative electron microscopy images of the hearts from the indicated genotypes of mice 4 wk after tamoxifen administration show defects in sarcomere organization, perturbed cardiac Z disks, a decrease in mitochondrial number, an increase in abnormal small mitochondria, and a substantial increase in glycogen deposits in mutant IDH hearts compared with controls. Arrows point to areas with massive glycogen deposits. Asterisks indicate autophagosomes. Bars show the indicated lengths and are the same across images on the same row. (M) Mitochondria; (N) nucleus; (S) sarcomere. (G,H) Mitochondrial quantification for the indicated genotypes. (G) Mitochondrial counts from the electron microscopy images; the number of images used for counts is 9, 6, and 11, respectively. (H) Real-time PCR for mitochondrial DNA in the hearts. All samples were normalized to genomic DNA of the same sample. n = 7 for all genotypes.