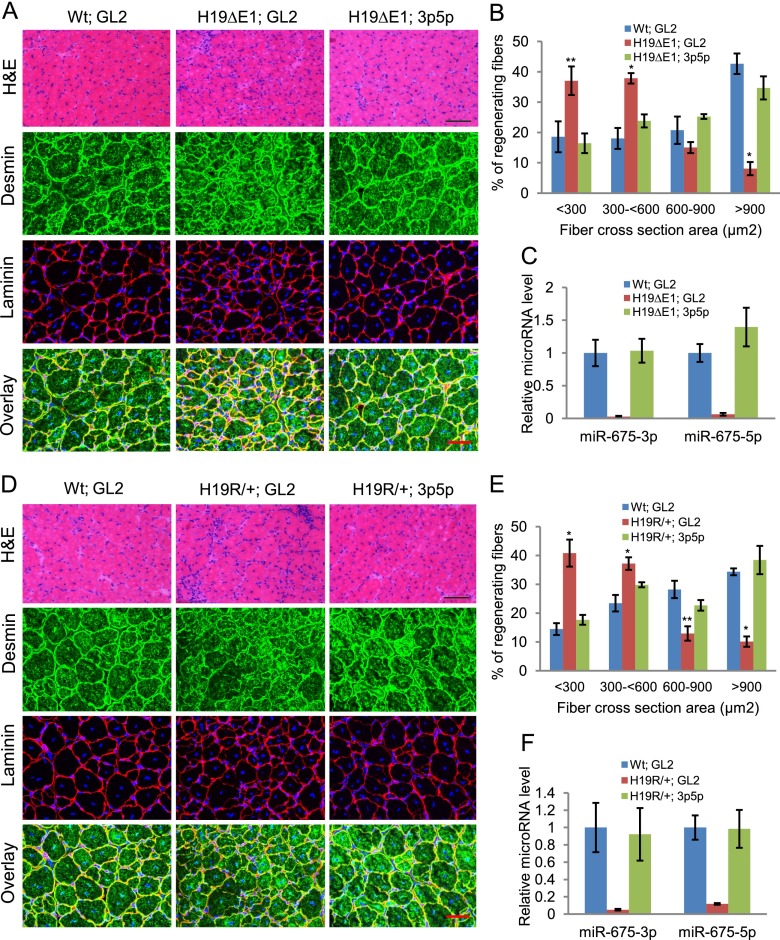
Figure 4.
H19 mutant mice show defects in muscle regeneration that can be rescued by exogenous miR-675-3p and miR-675-5p. (A) TA muscles in wild-type (Wt) or H19-deficient (H19ΔE1) littermates were injured by CTX injection and, after 3 d, were injected with miR-675-3p and miR-675-5p or with GL2 control microRNA in the contralateral leg. (Top panel) Representative H&E-stained images are from TA muscles harvested 14 d after CTX injury. Bar, 100 μm. (Bottom three panels) TA muscles from the same specimens were stained with desmin and laminin. Bar, 50 μm. Five mice were used in each group. (B) Cross-section areas of regenerating fibers of these samples were quantitated using Image J software. More than 200 individual fibers were counted in each group. (C) miR-675-3p and miR-675-5p levels were measured in these samples by qRT–PCR. (D–F) Data were obtained as in A–C from H19R/+ and control littermates. Bars: H&E, 100 μm; desmin and laminin, 50 μm. Mean ± SEM (n = 5). (*) P < 0.001; (**) P < 0.005. Note that the H19 mutations used in this study were specifically chosen because they do not disrupt imprinting of the adjoining Igf2 gene.