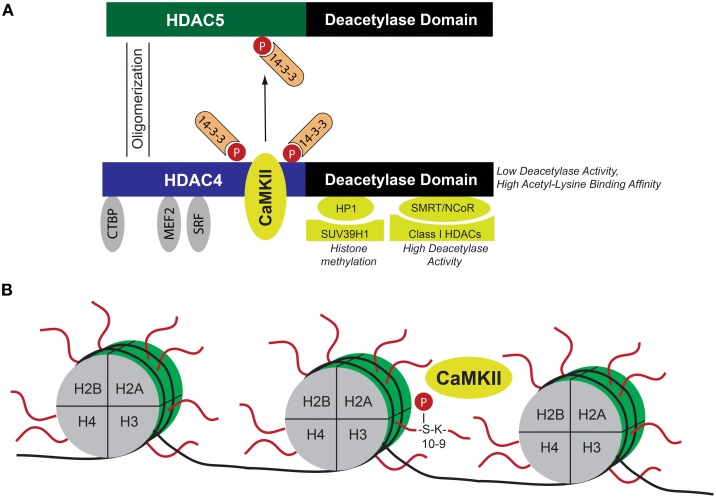
Figure 2.
Schematic of CaMKII-dependent epigenetic mechanisms. (A) HDAC4 as a nodal point for CaMKII-dependent epigenetic regulation. CaMKII binds to HDAC4 and phosphorylates HDAC4 at Ser-467 and Ser-632, leading to nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of HDAC4. When located in the nucleus, HDAC4 represses transcription factors such as MEF2, SRF, or the co-repressor CtBP. Binding to these transcriptional regulators directs HDAC4 to specific chromatin regions. HDAC4 recruits other chromatin modifying enzymes and direct them to the aforementioned specific chromatin regions. This results in CaMKII/HDAC4-dependent regulation of histone methylation (via interaction with HP1 and histone methyltransferase SUV39H1) and deacetylation (via interaction with SMRT/N-CoR and class I HDACs). Moreover, HDAC4 oligomerizes with HDAC5, and thereby induces 14-3-3 dependent nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of the HDAC4/HDAC5 complex, leading to de-repression of HDAC4/HDAC5-dependent transcription factors. Thus HDAC4 integrates CaMKII-dependent signals via epigenetic mechanisms. (B) Histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4) assemble with DNA to form nucleosomes. CaMKII directly phosphorylates Ser-10 in the N-terminal region of histone 3, which is located next to Lys-9, a major site for acetylation, and methylation. Phosphorylation at Ser-10 was suggested to result in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and increased chromatin binding of CaMKII at specific gene loci reactivated during cardiac hypertrophy. CaMKII Calcium/Calmodulin-dependent kinase II, CtBP C-terminal binding protein, HDAC histone deacetylase, HP1 heterochromatin protein 1, MEF2 myocyte elongation factor, N-CoR nuclear receptor co-repressor, SMRT silencing mediator of retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptor, and SRF serum response factor.