FIG 3 .
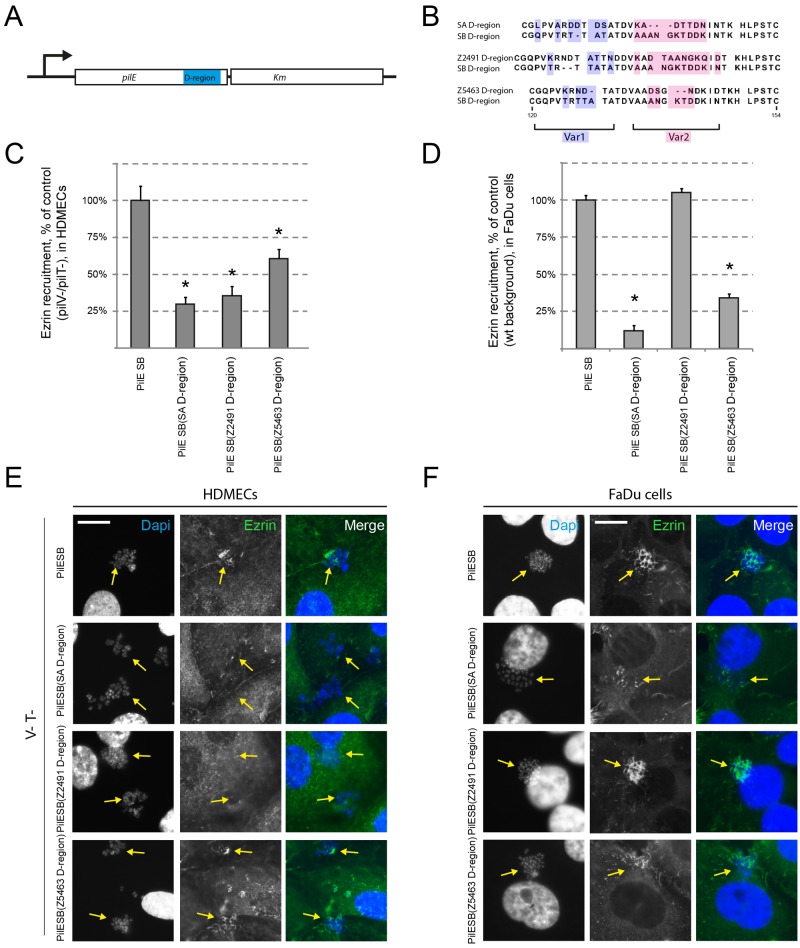
PilESB(D-region) variants are differentially involved in endothelial and epithelial cell responses. (A) Schematic representation of the PilE/Km transcriptional fusions used in this study. (B) ClustalW sequence alignment of the D-region of four different PilE variants: SB, SA, Z2491, and Z5463. Two variable domains (Var1 highlighted in blue and Var2 highlighted in red) were discriminated on the basis of alignment. (C, D, E, and F) HDMECs (C and E) and FaDu cells (D and F) were infected with strains of N. meningitidis expressing PilESB or PilESB(SA D-region), PilESB(Z2491 D-region), and PilESB(Z5463 D-region). HDMECs were infected with the PilV− PilT− derivatives of these strains. (C and D) The ezrin recruitment index was estimated by determining the proportion of colonies that efficiently recruit ezrin at the site of adhesion and expressed as normalized mean values (±SEM) of three independent experiments in duplicate. *, P < 0.002 (Student’s t test). (E and F) Ezrin was immunostained (in green), and DNA was stained using DAPI (in blue). Microcolonies are shown by arrows. Scale bars, 10 µm.