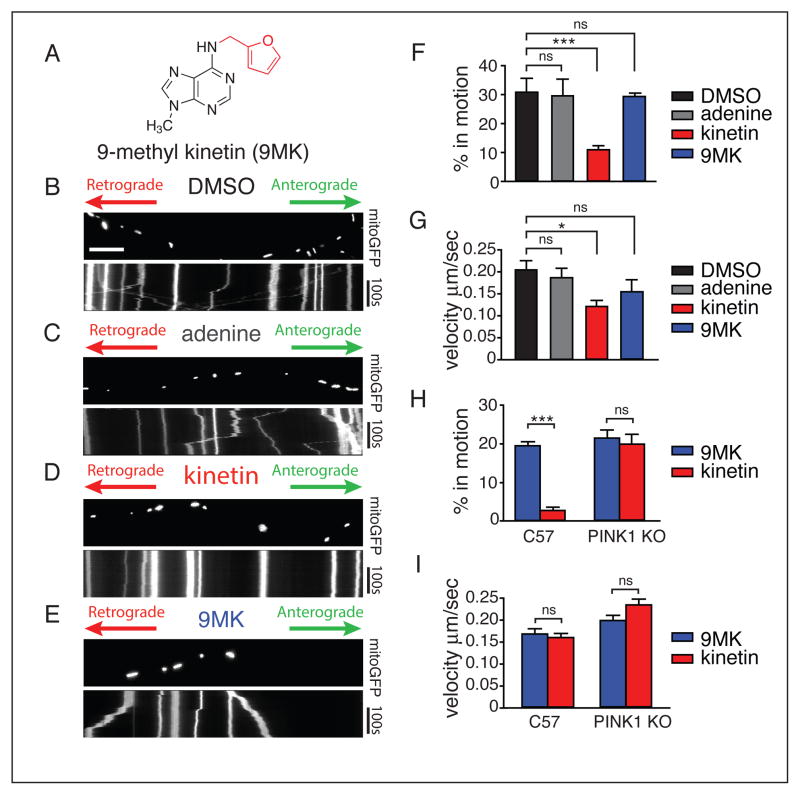
Figure 4. Kinetin halts axonal mitochondrial motility in a PINK1 dependent manner.
(A) Chemical structure of negative control non-metabolizable kinetin analog 9-methyl-kinetin
(B–E) Kymograph for analysis of mitochondrial movement in representative PINK1wt expressing rat derived hippocampal axons transfected with mitoGFP. Scale bar represents 10 μm.
(F) The percentage of time each mitochondrion was in motion was determined and averaged. Kinetin significantly blocks mitochondrial motility whereas 9MK has no effect (DMSO-kinetin, P=0.0005; DMSO-9MK, P=0.86)
(G) Kinetin induces a small decrease in velocity (DMSO-kinetin, P=0.03; DMSO-9MK, P=0.24).
(H) Kymograph for analysis of mitochondrial movement in C57BL/6 shows a response to kinetin (kinetin 9MK, P<0.0001), whereas in PINK1 knockout derived hippocampal axons kinetin has no effect (kinetin 9MK, P=0.64).
(I) Both kinetin and 9MK have no effect on mitochondrial velocity of moving mitochondrion (C57BL/6 kinetin-9MK, P=0.64; PINK1 KO, P=0.074) (all values are mean ± sem, analysis was two tailed students t-test)
See also Figure S5