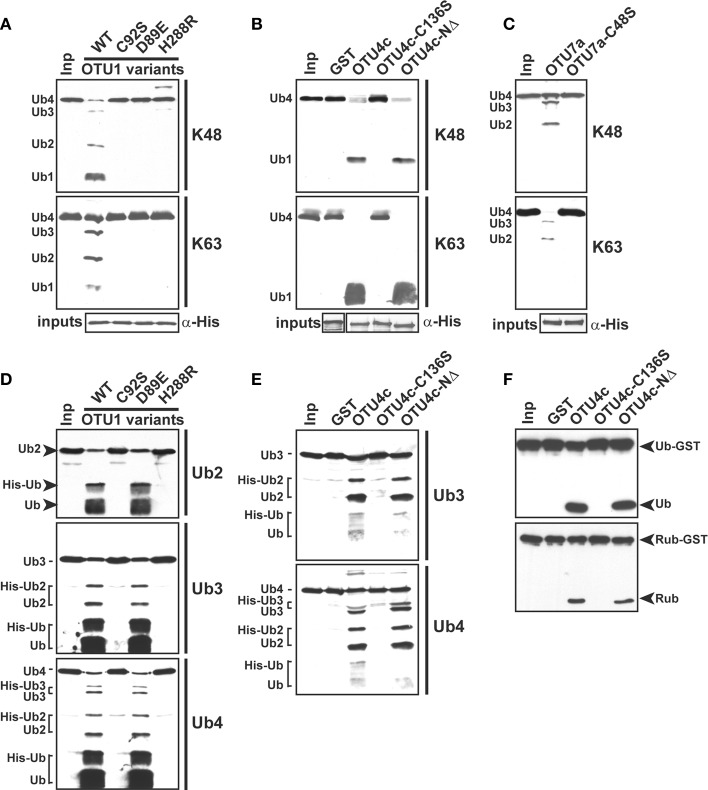
Figure 6.
The conserved catalytic triad is required for the deubiquitylation activities of A. thaliana OTU1, OTU4c, and OTU7a. (A)–(E) The catalytic roles of the conserved D89 in OTU1, the conserved catalytic triad in OTU1, OTU4c, and OTU7a, and the 43 N-terminal residues in OTU4c for cleavage of K48- and K63-linked UB tetramers (A)–(C), peptide bond-linked linear UB dimers (Ub2), trimers (Ub3), and tetramers (Ub4) (D,E), and peptide bond-linked UB- and RUB-GST fusions (F) were examined by comparing the cleavage activities of the site-specific or deletion mutants, which included the OTU1 variants C92S, D89E, and H288R; OTU4c-C136S; OTU4c-NΔ; and OTU7a-C48S, with those of the corresponding wild-type proteins. Substrates incubated without enzyme were used as negative input controls (Inp). The inputs and their cleavage products are labeled on the left or right and were visualized by immunoblotting with α-UB (A)–(E) or α-HA (F). Duplicate input OTU variants were detected by immunoblotting with antisera made against His-tag to confirm equivalent enzyme input levels (α-His). The His- (OTU1 and OTU7a variants) or His/GST-tagged (OTU4c variants) forms were used. GST was included as a negative control for the GST-fused OTU4c variants.