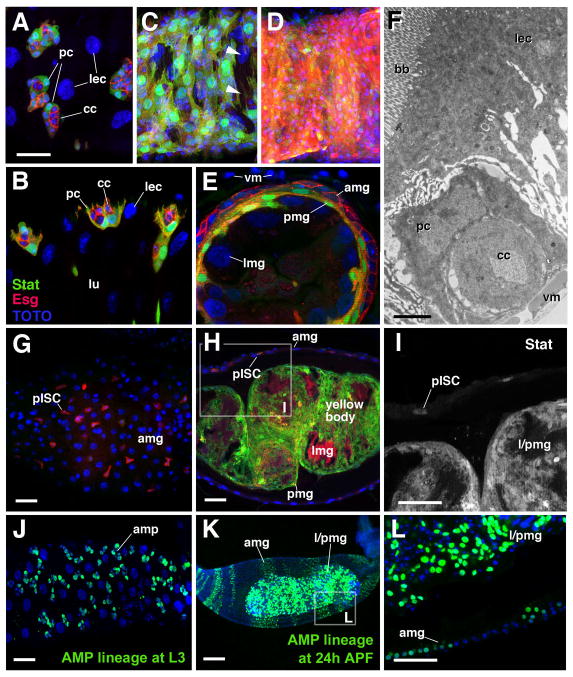
Fig. 2.
Formation of the transient pupal midgut. A–E: Z-projections of confocal sections of midgut of late third instar larva (L3; A, B), white prepupa (C), 6h prepupa (D, E), and 72h pupa (G–I). A, C, E and G present tangential confocal section of the outer gut epithelium; B, E and H show confocal cross sections. Adult midgut progenitors are labeled by esg-Gal4-driven mRFP (red) and by 10XStat92E-GFP (green; white in panel I). Cell nuclei are labeled by TOTO-3 (blue). A, B: clusters of small adult midgut progenitors form nests (nidi) scattered among large larval enterocytes (lec). Outer cells of each nest have differentiated into peripheral cells (pc) which express higher levels of 10XStat92E-GFP; central cells (cc) are small, round and Stat-negative. C: In white pre-pupa, the midgut contracts. Clusters of adult midgut progenitors approach each other and form a lose cell layer, still interrupted by gaps (arrowheads), that encloses the larval midgut epithelium. D, E: In the 6h pupa, peripheral cells and central cells of the former nests of adult midgut progenitors have fused into two complete layers. Central cells (Stat-negative, red) form the presumptive adult midgut (amg) at the outer surface; peripheral cells (Stat-positive, green) form the transient pupal midgut (pmg) underneath. In the center are the large larval midgut cells (lmg). Which undergo programmed cell death. Note that these cells express various levels of esg-Gal4 driven GFP throughout the pupal period. F: Electron micrograph of section of late larval midgut. At the top is a large larval enterocyte (lec) with a brush border (bb) of long microvilli at its apical surface. At the bottom is a nest of adult midgut progenitors, differentiated into central cells (cc) and peripheral cells (pc), and visceral muscle (vm).
G–I: In the 72h pupa, the degenerating larval midgut (lmg), surrounded and septated by the transient pupal midgut (pmg), has become the compact yellow body that rests in the lumen of the presumptive adult midgut (amg). 10xStat92-GFP is still expressed in the pupal midgut. In addition, it is expressed in the presumptive midgut stem cells (pISCs) which at this stage are scattered throughout the adult midgut layer. J–L: Lineage tracing experiments, activating a stably expressed lacZ reporter in adult midgut progenitors in the first instar larva by esg-Gal4 (see Material and Methods for detail). By late larval stage (J), adult midgut progenitors have proliferated and form clusters of 8–10 cells. In 24h pupa (K, L) labeled cells (descended from adult midgut progenitors) are found in both adult midgut (amg) and transient pupa midgut (pmg). amp adult midgut progenitors, bb brush border, cc central cells, lec larval enterocyte, lmg larval midgut, lu: lumen, pc peripheral cell, pmg pupal midgut, vm visceral muscle. Bars: 10μm (A–E; G–I; J; L); 2μm (F); 50μm (K)