Fig. 2.
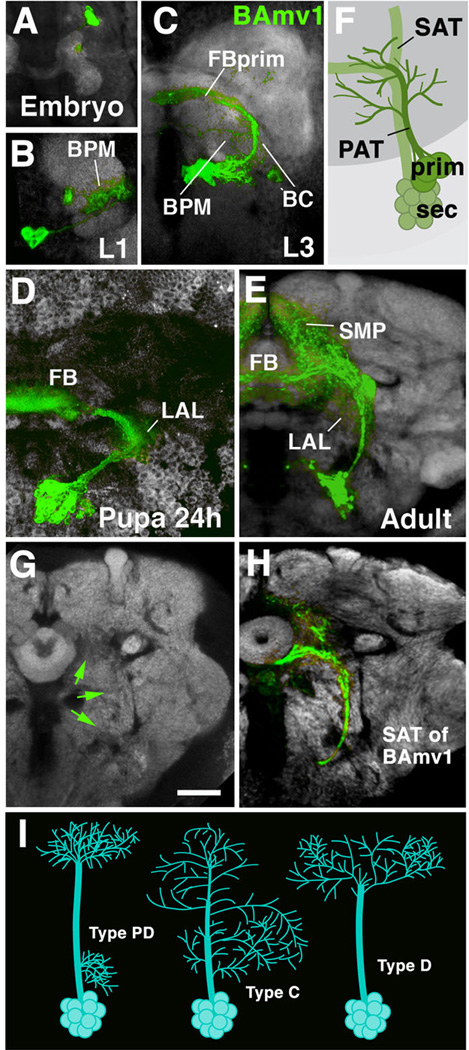
Morphogenesis of a brain lineage from embryo to adult. A-E: Z-projections of confocal sections of one brain hemisphere in which BAmv1 lineage is labeled by GFP driven by the line per-Gal4 (Kaneko and Hall, 2000). BAmv1 has a conspicuous crescent-shaped tract, projecting first posteriorly, then dorsolaterally, and finally dorso-medially towards the primordium of the fan-shaped body (FBprim), which forms part of the CPM compartment of the larval brain. Arborizations of primary neurons occur in BC, BPM and FBprim compartments (B, C). Secondary axons follow the same trajectory and branch in the lateral accessory lbe (LAL), fan-shaped body (FB), and superior medial protocerebrum (SMP; D, E). F: Cartoon illustrating that secondary axon tract (SAT) typically fasciculates with, or at least grows close to, primary axon tract (PAT) of the corresponding lineage. G, H: Secondary axon tracts develop into long fiber bundles of adult brain. G shows frontal confocal section of adult brain hemisphere labeled with anti-Bruchpilot (Nc82; neuropile; white). In H, the secondary neurons of the BAmv1 lineage are labeled by GFP (driven by per-Gal4). Note that the coherent secondary axon tract of BAmv1 now forms a long fiber bundle which is visible as a Nc82-negative (i.e., synapse-free) “tunnel”, indicated by green arrows in G.[SF1] I: schematic representation of different types of lineages encountered in Drosophila brain (PD: separate proximal and distal arborization; C: continuous arborization; D: distal arborization).
Bar: 20µm (all photographic panels at same scale)
