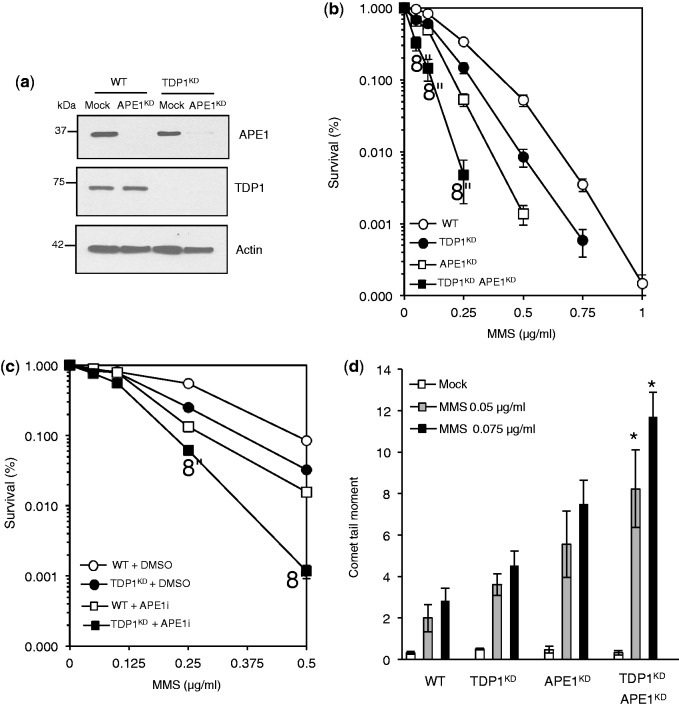
Figure 2.
Human cells depleted for TDP1 and APE1 exhibit synergistic hypersensitivity to MMS. (a) WT or TDP1KD MRC5 cells were subjected to control non-targeting siRNA ‘Mock’ or siRNA against human APE1. Cell extract was fractionated by SDS–PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-APE1 antibodies (Novus). (b) Control human MRC5 ‘WT’, TDP1KD, APE1KD or cells depleted for both APE1 and TDP1 ‘TDP1KD APE1KD’ were incubated with the indicated concentrations of MMS and percentage survival calculated from three independent replicates. Data are the mean ± s.e.m. Asterisks denote statistical difference (P < 0.01, t-test) between APE1KD and TDP1KD APE1KD cells (c) WT and TDPKD cells were incubated with DMSO or 150 μM of the APE1 inhibitor CRT0044876 ‘APEi’ for 2 h followed by an additional incubation with the indicated concentrations of MMS for 15 min at 37°C. Cell survival was calculated from the average of three independent experiments ± s.e.m. Asterisks denote statistical difference (P < 0.02; t-test) between mock and APEi-treated TDP1KD cells (d) MRC5 cells were incubated with the indicated doses of MMS for 15 min at 37°C and DNA SSBs and alkali labile sites quantified by alkaline comet assays. Average tail moment from 50 cells/sample was measured using Comet Assay IV software (Perceptive) and data are the average ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments. Asterisks denote statistical difference (P < 0.05; t-test) between APE1KD and TDP1KD APE1KD cells.