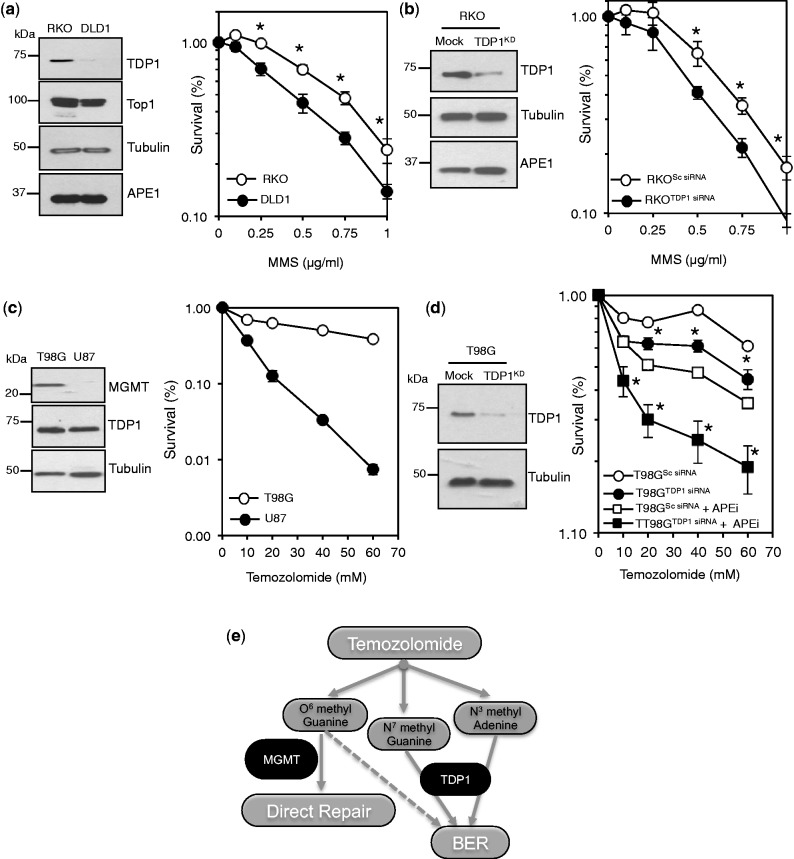
Figure 9.
TDP1 depletion sensitizes glioblastoma-resistant cancer cells to temozolomide. (a) Cell lysates from RKO and DLD1 cancer cell lines were fractionated by SDS–PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-TDP1 (Eurogentec), anti-Top1 (Santa Cruz), anti-Tubulin (Abcam) and anti-APE1 (Novus) antibodies (left). RKO and DLD1 cells were compared for their survival following exposure with the indicated doses of MMS for 15 min at 37°C (right). Data are the average of three independent experiments ± s.e.m. Where not visible, error bars are smaller than the symbol. (b) RKO cells were subjected to scrambled siRNA (Mock) or siRNA against TDP1 (TDP1KD) and cell lysates analyzed by immunoblotting (left). Control RKO (RKOSc siRNA) and RKO cells in which TDP1 levels were depleted (RKOTDP1 siRNA) were examined for their survival following exposure to the indicated doses of MMS, as described earlier in the text (right). (c) Glioblastoma multiforme T98G and U87 cancer cell lines were analyzed for methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT) expression using anti-MGMT antibodies (Abcam) (left). High-MGMT expressing T98G cells were compared with low-MGMT expressing U87 cells for their survival following exposure to increasing concentrations of the alkylating agent temozolomide (right). (d) TG98 cells were subjected to scrambled siRNA (Mock) or siRNA against TDP1 (TDP1KD) and cell lysates analyzed by immunoblotting (left). Control T98G cells (T98GSc siRNA) and cells in which TDP1 levels were depleted (TG98TDP1 siRNA) were incubated with DMSO or 150 μM of the APE1 inhibitor CRT0044876 ‘APEi’ for 2 h followed by additional incubation with the indicated concentrations of MMS for 15 min at 37°C. Cell survival was blindly scored from three independent biological repeats, and data are the average ± s.e.m. (right). (e) Model for the repair of temozolomide-induced DNA breaks. Temozolomide delivers a methyl group to purine bases of DNA, resulting in O6-methyl guanine, N7-methyl guanine and N3-methyl adenine. The primary cytotoxic lesion is believed to be O6-methyl guanine, which can be removed by a direct repair mechanism mediated by methylguanine methyltransferase (MGMT). Inherent and acquired resistance to temozolomide via MGMT expression presents a major challenge in cancer therapy, particularly for glioblastoma multiforme. TDP1 promotes the repair of methylated purines induced by temozolomide via a distinct non-canonical BER pathway. Increasing the load of unrepaired methylated purines by exploiting the limited availability of TDP1 alone or in combination with canonical BER factors such as APE1 provides a new synthetic lethal setting to improve the clinical outcome of temozolomide-based cancer therapy. Asterisks denote statistical differences (P < 0.05; t-test) between control and TDP1-deficient cells.