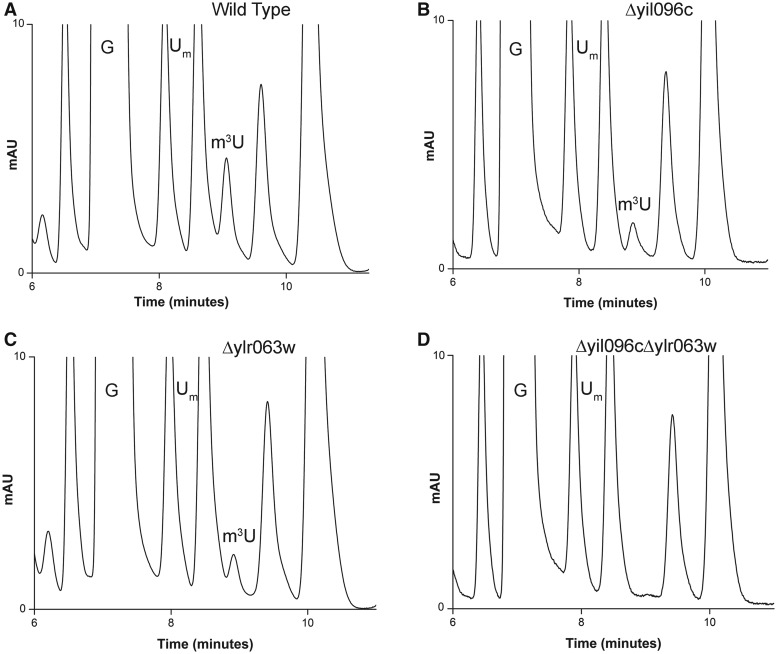
Figure 1.
RP-HPLC screening of the mutants for identification of m3U methyltransferase. The 25S rRNA from mutants and isogenic wild type were digested to nucleosides using P1 nuclease and alkaline phosphatase. Nucleosides obtained after digestion was then analyzed by RP-HPLC. For optimum separation of m3U residues, we changed the elution conditions to an isocratic mode using 50% buffer A (2.5% methanol) and 50% buffer B (20% methanol). RP-HPLC chromatogram from the wild type (A), Δyil096c (B), Δylr063w (C) and Δyil096cΔylr063w (D) mutants. The peak corresponding to the m3U with a retention time of ∼9 min reduces to half in both Δyil096c and Δylr063w mutants and disappears in double mutant Δyil096cΔylr063w, highlighting the involvement of these two methyltransferases in m3U methylations of the 25S rRNA.