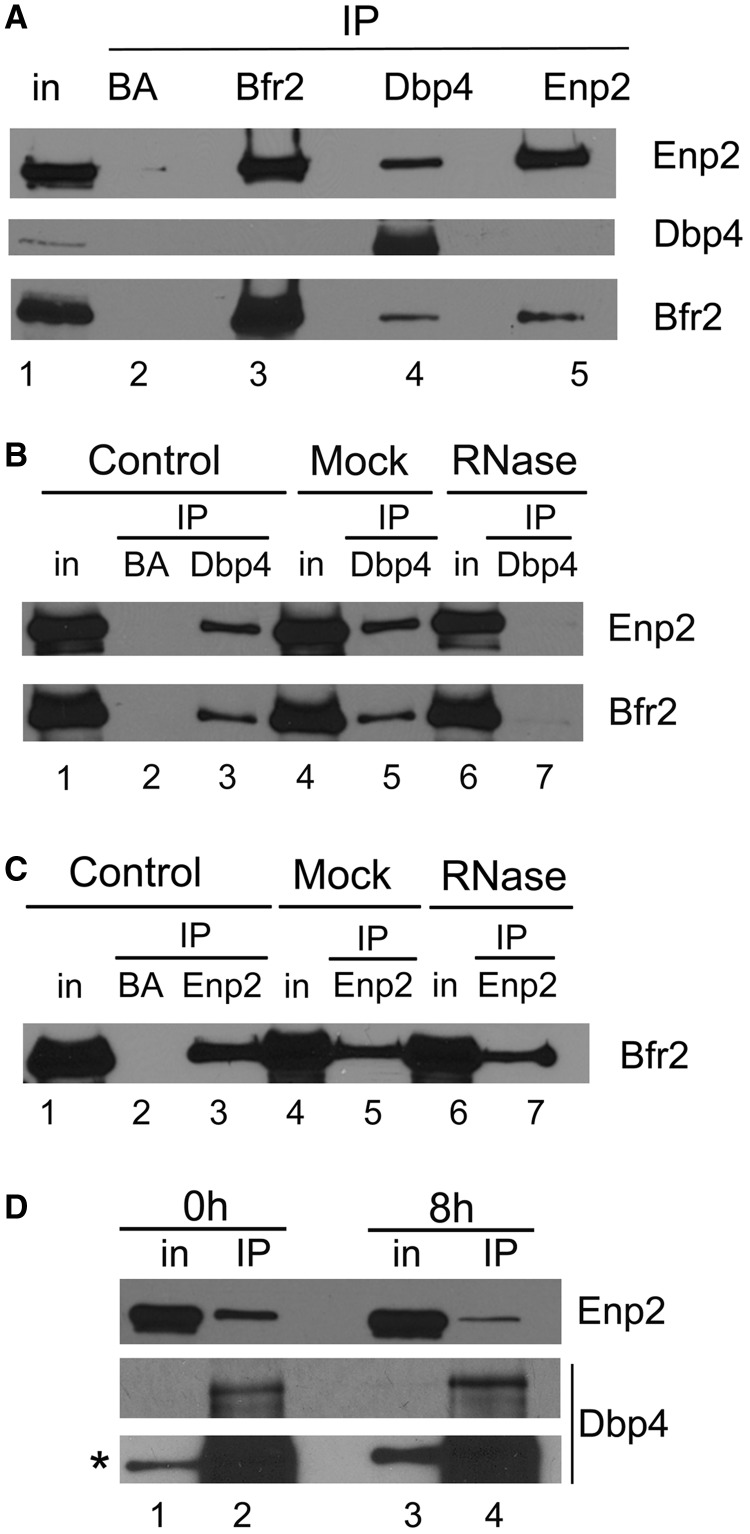
Figure 3.
Analyzing interaction between Bfr2, Dbp4 and Enp2 by IPs. (A) Dbp4 associates with Bfr2 and Enp2 in vivo. IPs were carried out with anti-HA, anti-myc and anti-Dbp4 antibodies using extracts prepared from the double-tagged strain that expresses HA-tagged Bfr2 under the control of the GAL1 promoter and myc-tagged Enp2 from its natural promoter. Control IPs were done in absence of antibodies (beads alone, BA). Lane 1 is whole cell extract (T is 6.5% input), and lanes 2–5 are IPs with beads alone (BA), anti-HA mAb (Bfr2), anti-Dbp4 antibodies and anti-myc mAb (Enp2). The same blot was subjected to immunodetection with various antibodies recognizing proteins identified on the right. (B) Dbp4 associates with Bfr2 and Enp2 in an RNA-dependent manner. Control IPs (lanes 1–3) were done as in Figure 3A. In the mock (lanes 4–5), the cellular extract was incubated at 37°C for 10 min before IP, and in lanes 6 and 7 the cellular extract was treated with RNase A for 37°C for 10 min. IPs were done in absence of antibodies (BA, lane 2) or with anti-Dbp4 antibodies (lanes 3–7), and immunoblotting was performed using anti-myc (Enp2) and anti-HA mAbs (Bfr2). T is 6.5% of input. (C) Association of Bfr2 with Enp2 is not RNA-dependent. IPs were carried out as in Figure 3B, except that anti-myc mAb (Enp2) was used for IP, and immunodetection was performed with anti-HA mAb (Bfr2). T is 6.5% of input. (D) Bfr2 is required for the association of Dbp4 with Enp2. Cellular extracts were prepared from undepleted cells (0 h, lanes 1–2) or Bfr2-depleted cells (8 h, lanes 3–4). IPs were carried out with anti-Dbp4 antibodies and western blotting analyses for Enp2 and Dbp4 were done with anti-myc mAb and anti-Dbp4 antibodies, respectively. The asterisk indicates the overexposed blot. T is 6.5% of input.