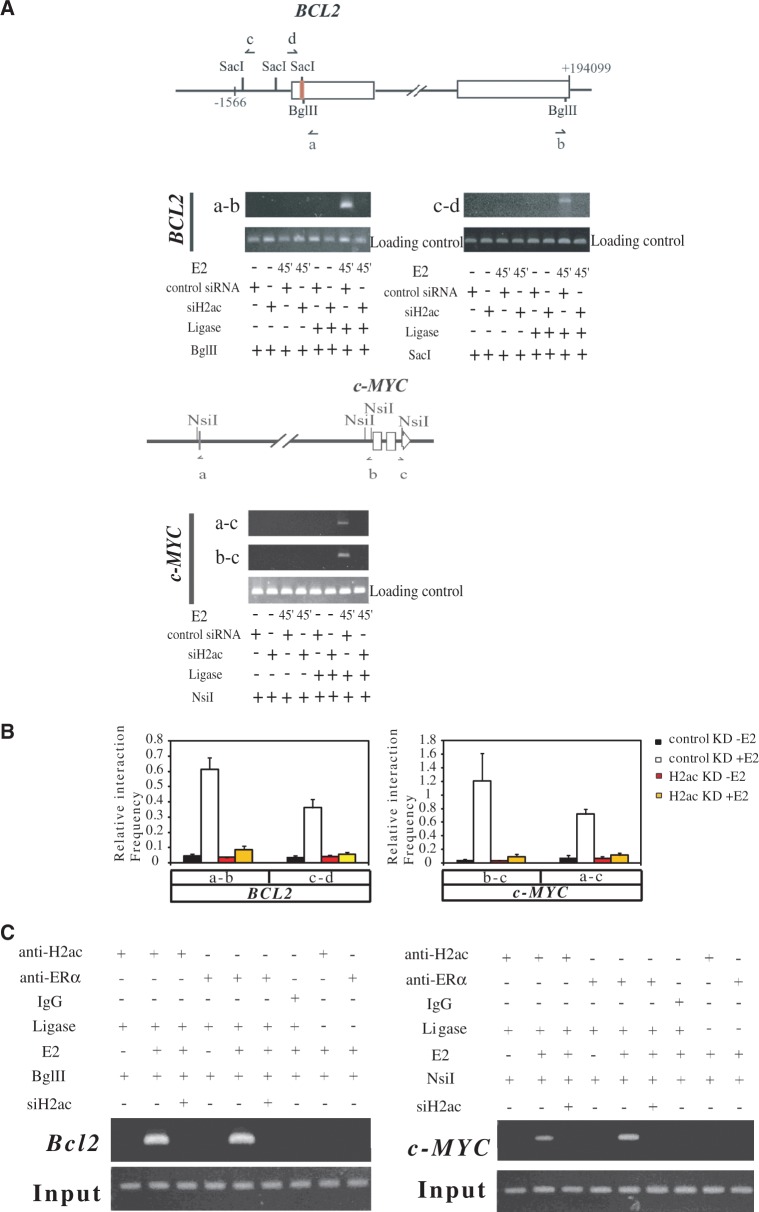
Figure 7.
H2ac is required for the recruitment of ERα via loop formation. (A) Upper panel: Schematic diagram of the BCL2 and c-MYC genes showing the coding region (open boxes), and enhancers (red bars).The restriction sites and the orientation of the 3C primers (arrows) for PCRs in 3C experiments are shown. Lower panel: 3C assays showing the presence in MCF-7 cells of the specific 3C products from the BCL2 gene and from the c-MYC gene under conditions with or without H2ac knockdown. The experiments involved formaldehyde (CH2O) cross-linking and ligation of the samples in absence or presence of estradiol for 45 min. The loading control primers are shown in Supplementary Table S3. (B) Quantitative histograms of the 3C assays. Relative cross-linking frequencies are shown for the different ligation products that were quantified using primer pairs targeting the promoters, enhancers and 3′UTRs of BCL2 and c-MYC. These were compared with a control primer pair and carried out under conditions with or without H2ac knockdown in absence or presence of estradiol for 45 min. Data represent mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments. (C) ChIP-3C analysis of the enhancer-3′UTR association of BCL2 and of c-MYC. ChIP-3C assays were performed using H2ac and ERα specified antibodies to immunoprecipitate cross-linked chromatin from MCF-7 cells treated with E2 or either vehicle for 45 min; the products were then digested with Bgl II or Nsi I, followed by a ligation reaction in the presence or absence of DNA ligase. a–b primer pair for BCL2 and a–c primer pair for c-MYC. The enhancer region of BCL2 was used as an input control.