Fig.3.
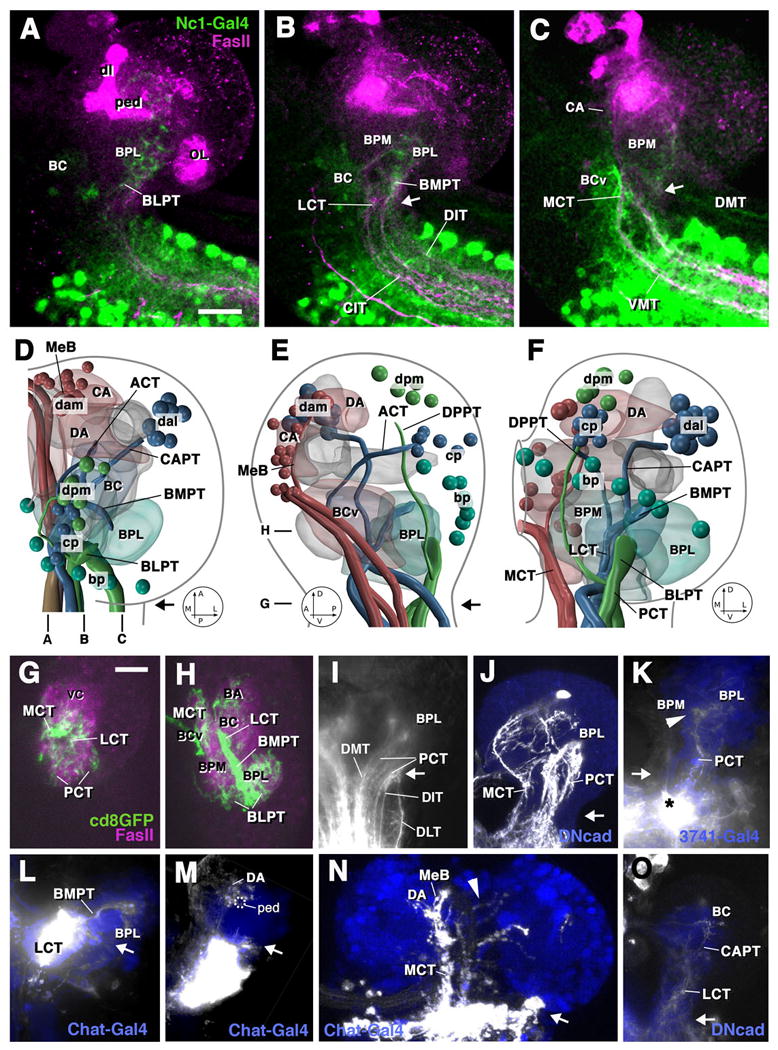
Ascending projections into the first instar brain. A-C: Z projections of parasagittal confocal sections of brain and anterior ventral nerve cord of preparation in which GFP is driven by the Nc1-Gal4 driver line which is expressed in most, if not all, neurons of the ventral nerve cord from thoracic levels posteriorly (green label). An antibody against FasII labels long axon tracts (red). Levels of sections are indicated at bottom of panel D. Arrows in these and all other panels indicate boundary between brain and ventral nerve cord. Ascending projections reach mainly the basal compartments of the brain neuropile. Laterally (A), ascending fibers enter the BLP compartment via BLPT. At intermediate level (B), fibers ascending via CIT/DIT tracts, continuing through BMPT, carry input to BC and lateral BPM. At a medial level (C), fibers ascending via the VMT and DMT tracts terminate in the BCv, CA, and BPM compartments. D-F show digital 3D models of right brain hemisphere in dorsal view (D; anterior to the top), medial view (E; anterior to the left), and posterior view (F; medial to the left). Groups of descending neurons, long axon tracts carrying ascending and descending fibers, and neuropile compartments receiving ascending input are color coded and annotated as in the models shown in Fig.2M-O. G, H: horizontal confocal sections of right brain hemisphere of preparation where GFP (green) is expressed in large clones of ventral nerve cord neurons. Neuropile is labeled red by anti-DNcad. The levels of sections are indicated to the left of panel E. G shows horizontal confocal section at level of brain-ventral nerve cord boundary. Ascending fibers are highly concentrated in MCT and LCT; the PCT appears more spread out, consisting of several thin fascicles arranged along the posterior surface of the neuropile. At the slightly more dorsal level shown in H, the LCT gives rise to the BMPT which carries ascending fibers into the BPL compartment from anteriorly, whereas PCT afferents (forming the BLPT tract at this level) reach the BPL from posteriorly. Note scattering of terminal fibers also in BCv, BC and BA compartments.
I-O: Z-projections of confocal sections of brain preparations in which ascending fibers are labeled by injection of DiI or clonal expression of GFP. Backfilled fibers and cells appear white. Blue color shows cells of the cortex or neuropile labeled by expression of GFP reporter gene driven by Chat-Gal4 or 3741-Gal4. Note varicose endings (“boutons”) of labeled axons in K, M, and N, which is typical of axonal terminations. I: Large injection into dorsal part of ventral nerve cord, labeling ascending fibers in all three dorsal tracts (DMT, DIT, DLT). These fibers continue on their parallel course, forming the spread-out PCT that carries the fibers towards the BPL compartment. J: Clones of ventral nerve cord neurons projecting ascending fibers into the basal brain via PCT and MCT. K: Ascending fibers terminating in BPL and BPM compartments, labeled via small DiI injection into dorsal tier of ventral nerve cord. L: Labeling of fibers ascending through BMPT into BPL compartment. M, N: Ascending fibers reaching the DA compartment via MCT and median bundle. A small number of fibers crosses to the contralateral hemisphere in the brain commissure (arrowhead in N). O: Small contingents of fibers ascending through LCT and CAPT towards BC compartment. Other abbreviations: dl dorsal lobe of mushroom body; MeB median bundle; OL optic lobe; ped peduncle of mushroom body; vc ventral nerve cord Bars: 10μm (for A-C; G-O)
