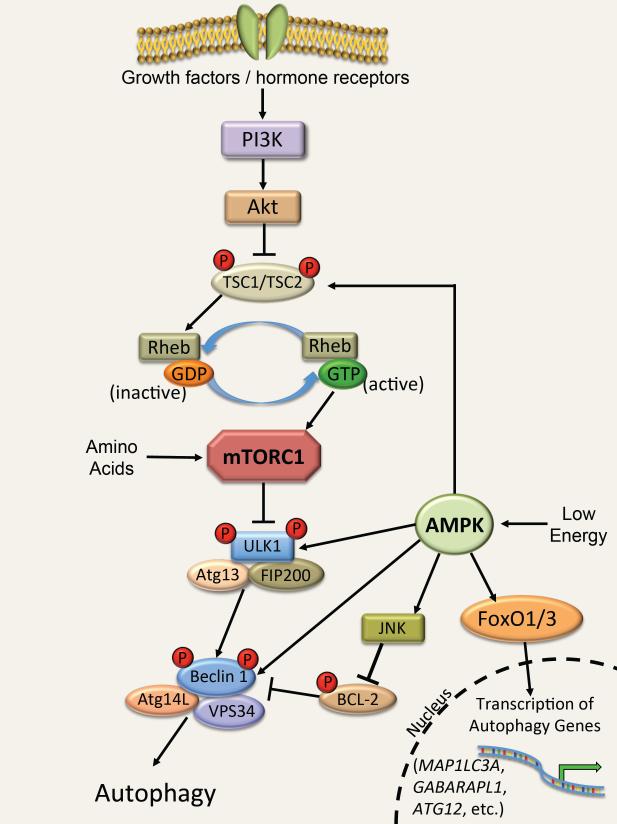
Figure 1.
Regulation of autophagy by mTOR and AMPK
Insulin and growth factors signal through phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and Akt to inhibit the tuberous sclerosis (TSC)1/2 complex. Inhibition of this complex allows active Ras homolog enriched in brain (RHEB)-GTP to activate mTOR in the mTORC1 complex, leading to phosphorylation of the ULK1 complex and inhibition of autophagy. Amino acids can also activate the mTORC1 complex by a separate mechanism. AMPK responds to low cellular energy levels by activating ULK1 via phosphorylation, resulting in activation of autophagy. Additionally, AMPK can initiate autophagy by disrupting Bcl-2 inhibition of Beclin 1, by activating forkhead box protein O (FoxO) transcription factors, and by directly activating TSC1/2 and Beclin 1.