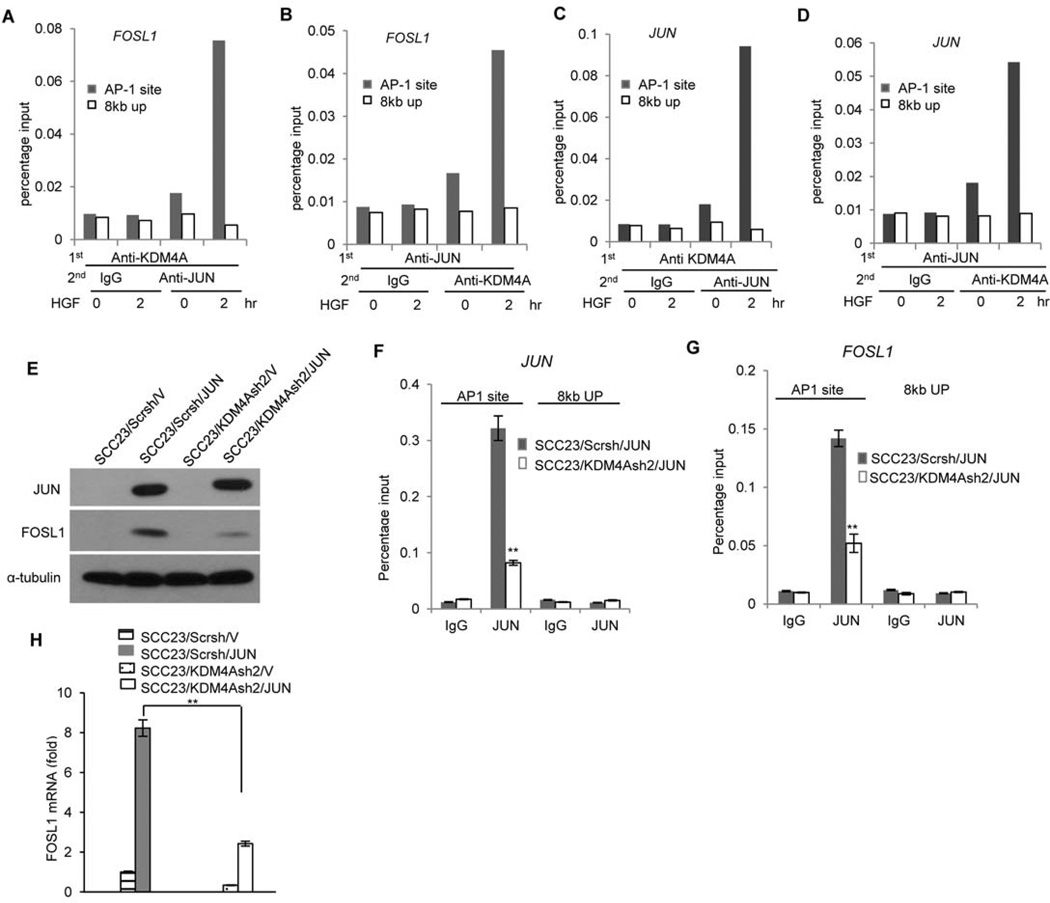
Fig 6. Histone demethylation by KDM4A is required for the recruitment of JUN/AP-1 to the target gene promoter.
(A and B) Reciprocal re-ChIP assays of the co-occupancy of JUN and KDM4A on the FOSL1 promoter in FaDu cells treated with 20 ng/ml HGF for up to 2 hours. Data represent three independent experiments. (C and D) Reciprocal re-ChIP assays of the co-occupancy of JUN and KDM4A on the JUN promoter as described in (A) and (B). Data represent three independent experiments. (E) Western blot analysis of JUN and FOSL1 abundance in SCC23 cells overexpressing JUN (Scrsh/JUN), depleted of KDM4A (KDM4Ash2/V), or overexpressing JUN in a KDM4A-depleted background (KDM4Ash2/JUN) compared with control cells (Scrsh/V). Blot is representative of 2 experiments. (F and G) ChIP assays of JUN abundance on the (F) JUN or (G) FOSL1 promoter either at the AP-1 binding site or 8 kb upstream in SCC23 cells overexpressing JUN (Scrsh/JUN) compared with those also depleted of KDM4A (KDM4Ash2/JUN). **P<0.01, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (n = 3). (H) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of FOSL1 expression in cells as described in (E). **P<0.01, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test (n = 3).