Fig. 1. Single-Cys replacements tested in this study.
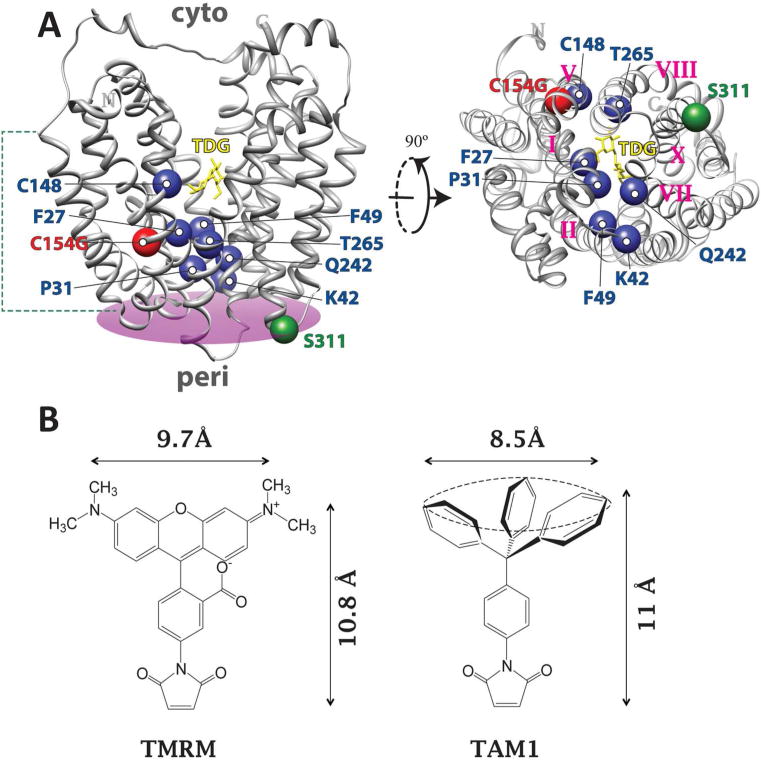
(A) Left, the structure of C154G LacY (PDB ID: 1PV7) viewed from the side with the N-terminal 6-helix bundle on the left and C-terminal 6-helix bundle on the right. TDG is shown as yellow stick at the apex of the central cavity. The Cα carbons of F27 (helix I), P31 (helix I), K42 (helix II), F49 (helix II), C148 (helix V), Q242 (helix VII) and T265 (helix VIII) are superimposed on the backbone of C154G LacY as blue spheres. A plane was defined (colored in purple) based on the position of five helix-terminal residues (D36, Q100, Q256, T310 and E374) on the periplasmic side of LacY to define the border of the coherent structural domain. The distance of each Cα carbon to the periplsmic side of LacY is measured as the distance from each Cα carbon to the defined plane on the periplamic side of LacY: 27, 15 Å; 31, 8 Å; 42, 4 Å; 49, 13 Å; 148, 25 Å, 242, 9 Å; 265: 14 Å. The Cα carbon of G154 (helix V) and S311 (helix X) are presented as red and green spheres, respectively. The green dashed lines indicate the dimension of the cytoplasmic membrane. Right, the image of LacY on the left side is turned 90° and viewed from the periplasmic side. Roman number labels the helices where the single-Cys replacements are located. (B) The chemical structures of TMRM and TAM1.