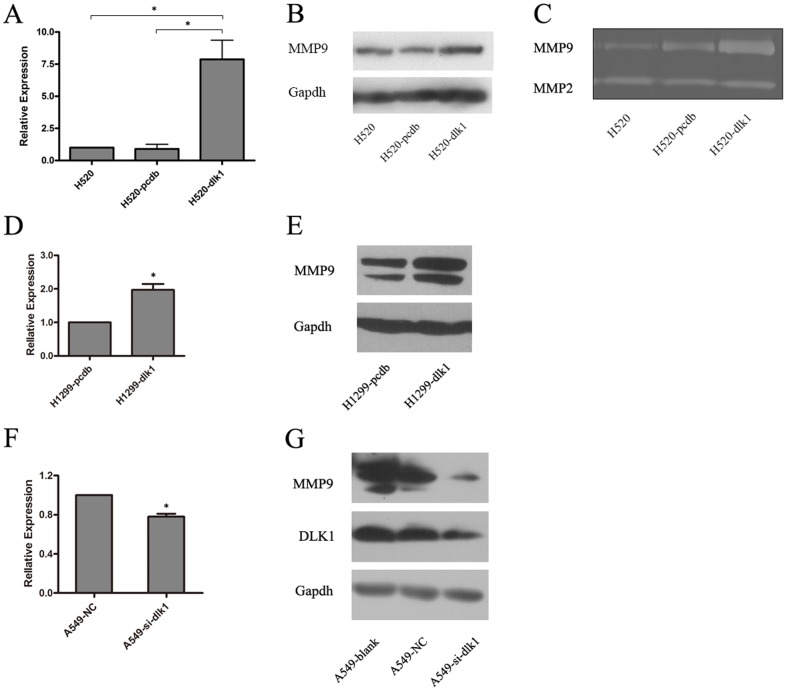
Figure 2. Effect of DLK1 on the expression and activity of MMP9 in human lung cancer cell lines.
A, a histogram for the relative mRNA expression of MMP9 in H520 cells transfected with DLK1 (H520-dlk1) or null vector (H520-pcdb) detected by real-time PCR analysis. The expression level of MMP9 in the blank H520 cells was used as a control and set to 1. B, the protein expression of MMP9 in H520-dlk1, H520-pcdb and H520 cells evaluated by Western blotting analysis. C, gelatin zymography showing the activity of secreted MMP9 and MMP2 in H520-dlk1, H520-pcdb and H520 cells. D, real-time PCR analysis of the relative mRNA expression of MMP9 in H1299 cells transfected with DLK1 (H1299-dlk1) or null vector (H1299-pcdb) shown in a histogram. E, Western blotting showing the protein expression of MMP9 in H1299-dlk1 and H1299-pcdb cells. F, a histogram showing the relative mRNA expression of MMP9 in DLK1 siRNA (A549-si-dlk1) or null control siRNA (A549-NC) transfected A549 cells evaluated by real-time PCR analysis. G, the protein expression of MMP9 in A549-si-dlk1, A549-NC and blank A549 cells detected by Western blotting. All of the experiments were performed in triplicate. 18S ribosomal RNA was used as an internal control in the real-time PCR analysis, whereas GAPDH was used as an internal control in the Western blotting analysis (* t-test, p-value <0.05).