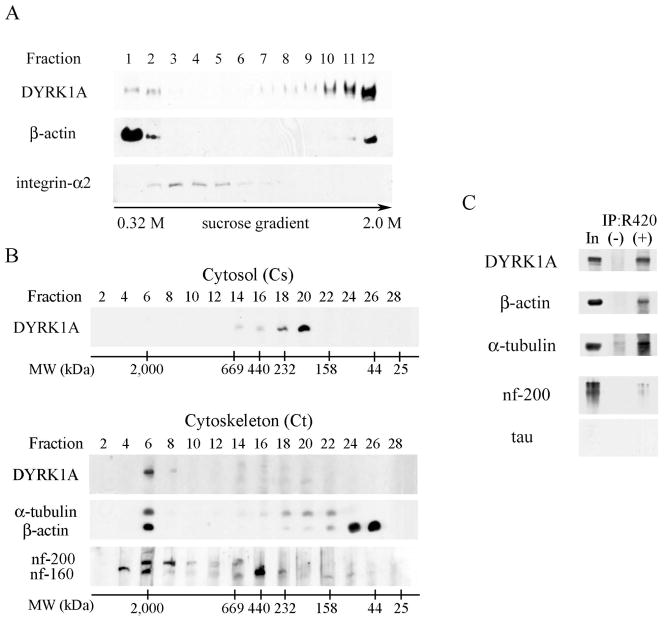
Fig. 3.
A: Sucrose density fractionation of postnuclear supernatant in the presence of non-ionic detergent (1% TX-100) revealed weak DYRK1A immunoreactivity in detergent-soluble fractions 1 and 2 (containing cytosol proteins) and a strong immunoreactivity in β-actin–rich and detergent-resistant fractions 11 and 12 (cytoskeletal proteins). Fractions 3–5 enriched in membrane lipid rafts (shown by the presence of integrin-α2) did not contain DYRK1A. Equal vols of 20 μL of each fraction were loaded per lane. B. To estimate the size of DYRK1A, 100,000 × g supernatant (cytosol) and 100,000 × g pellet (cytoskeleton fraction) were subjected to gel filtration on Superose 6. Cytosolic DYRK1A that peaked in fractions 18–20 comprised proteins in the range of 232–158 kDa (upper panel). DYRK1A from the detergent-resistant cytoskeletal fraction (lower panel), solubilized in 8 M urea and subjected to gel filtration on Superose 6, peaked in fraction 6 and comprised protein complexes larger than 2,000 kDa and cytoskeletal proteins: neurofilament heavy (nf-200) and medium (nf-160), α-tubulin, and β-actin. Images of mAb 8D9–detected Western blots are shown with the position of molecular weight markers of 2,000, 669, 440, 232, 158, 44, and 25 kDa. C: Western blots of DYRK1A immunoprecipitates revealed several cytoskeletal proteins co-precipitated with DYRK1A. The material immunoprecipitated with pAb R420 was divided in five equal parts to detect DYRK1A (mAb 8D9), β-actin, α-tubulin, heavy neurofilament, and tau proteins in WB. Non-immune rabbit IgG—a specificity control of IP—is shown in lane (−), lane In marks 10% of the reaction input.