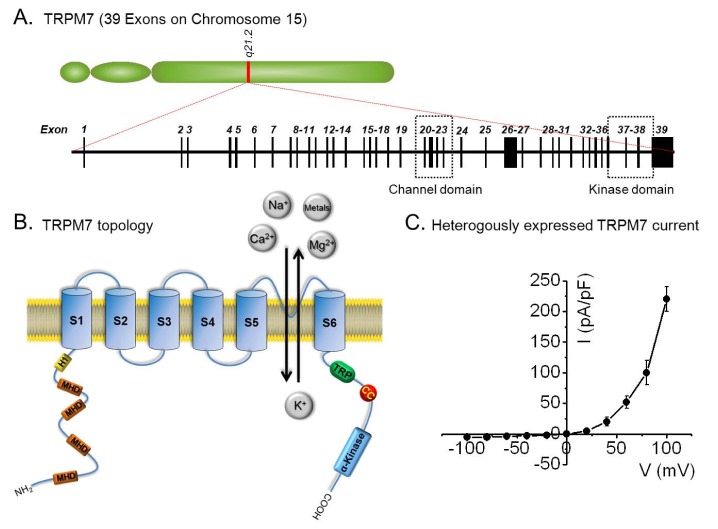
Fig. 1.
Structure and electrophysiological features of TRPM7. (A) The TRPM7 gene is located on chromosome 15 and consists of 39 exons. The boxes highlight the sequence regions corresponding to the channel and kinase domains. (B) Diagram showing the putative membrane topology of a single TRPM7 subunit. Each TRPM7 subunit contains six transmembrane segments and a pore-forming loop between S5 and S6. Its cytoplasmic N-terminus contains another hydrophobic region (H1) and four TRPM homology regions (MHD), whereas its C-terminal intracellular region contains a TRP box, conserved residues after the last transmembrane segment, and a coiled-coil (CC) region before its alpha-kinase. The distal C-terminus has an atypical serine/threonine protein kinase domain. As indicated in the figure, TRPM7 is a non-selective cation channel that conducts both monovalent ions, such as, Na+ and K+, and divalent ions, such as, Ca2+, Mg2+, and other trace metal ions. (C) Representative current-voltage (I-V) relationship obtained using the whole-cell patch clamp technique in HEK-293 cells expressing mouse TRPM7. TRPM7 currents are characterized by pronounced outward rectification and a small inward current in the presence of normal external concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+.