Figure 7.
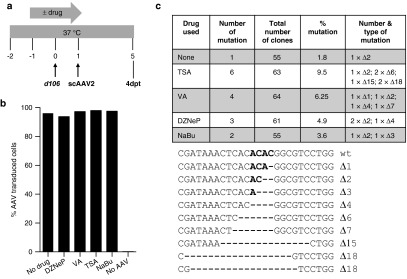
Targeted mutagenesis in herpes simplex virus (HSV)-infected cells treated with histone deacetylase inhibitor (HDACi). (a) Schematic of experimental timeline. MRC5 cells were infected with recombinant HSV-1 d106 at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.5 in the absence or presence of drug, transduced with scAAV2 at a MOI of 5 × 104 genomes/cell/vector in the absence of drug for 4 days prior to analysis for mutational events. (b) Flow cytometry for green flourescent protein (GFP) fluorescence in control uninfected MRC5 cells cultured in the absence (no drug) or presence of the indicated HDACi for 2 days, then either left untransduced (no AAV) or transduced with scAAV2-GFP and scAAV2-Trex2 at a MOI of 5 × 104 genomes/cell/vector for 4 days in the absence of drug. (c) HSV1m5 target sequence analysis. The HSV region containing the HSV1m5 target site was PCR amplified using total genomic DNA obtained at 4 days post-AAV transduction from d106-infected MRC5 exposed to HSV1m5 and Trex2 in the absence (none) or presence of the indicated HDACi. PCR amplicons were cloned and sequenced from individual bacterial colonies. The percent and nature of mutations in the HSV1m5 target site are shown. wt, wild-type sequence of the HSV1m5 target site. Bold indicates the four nucleotides constituting the 3′ overhang generated by the DNA DSB. Δ: deletion. HDACi used: trichostatin A (TSA 100 nmol/l), valproic acid (VA 1 mmol/l), 3-deazaneplanocin (DZNep 5 µmol/l), sodium butyrate (NaBu 5 mmol/l).
