Figure 1.
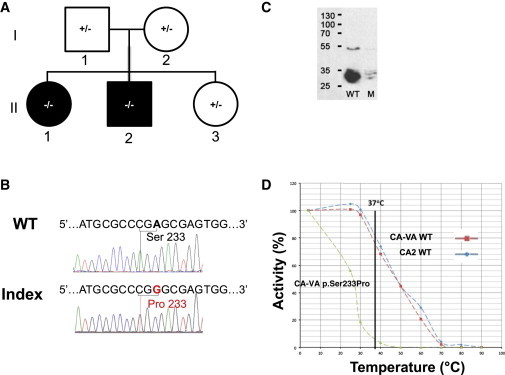
Family 1 with p.Ser233Pro Missense Variant
(A) Pedigree (black fill indicates clinically affected individuals, II-1 and II-2).
(B) Sanger sequence of CA5A from index (II-1) and control (wild-type sequence; WT) subjects; the variant nucleotide position and the corresponding codon alteration (p.Ser233Pro) are indicated.
(C) Immunoblot analyses by SDS-PAGE (ImageJ software) of WT and p.Ser233Pro (mutant; M) CA-VA protein levels in COS-7 cell lysates; the molecular weights (kDa) of protein standards are indicated on the left. Normal and mutant (c.697T>C) CA5A cDNAs, including the full mitochondrial targeting sequences, were synthesized via the NCBI reference sequence (NM_001739.1) by Genscript. The cDNAs were cloned into pUC57 at XhoI and BglII sites and verified by Sanger sequencing. Subsequently, the cDNA inserts were subcloned via the same restriction sites into the pCXN mammalian expression vector. COS-7 cells (ATCC CRL-1651) were transfected with wild-type or mutant CA5A plasmids with Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s protocol, as previously described.8 A β-glucuronidase expression plasmid was cotransfected as a marker of transfection efficiency.24 COS-7 cells were harvested 48–72 hr after transfection in lysis buffer and then lysed by sonication on ice.
(D) Thermal stability profiles for WT (red) and p.Ser233Pro mutant (green) CA-VA enzymes. Carbonic anhydrase II (CA2; blue) was used as a control.
