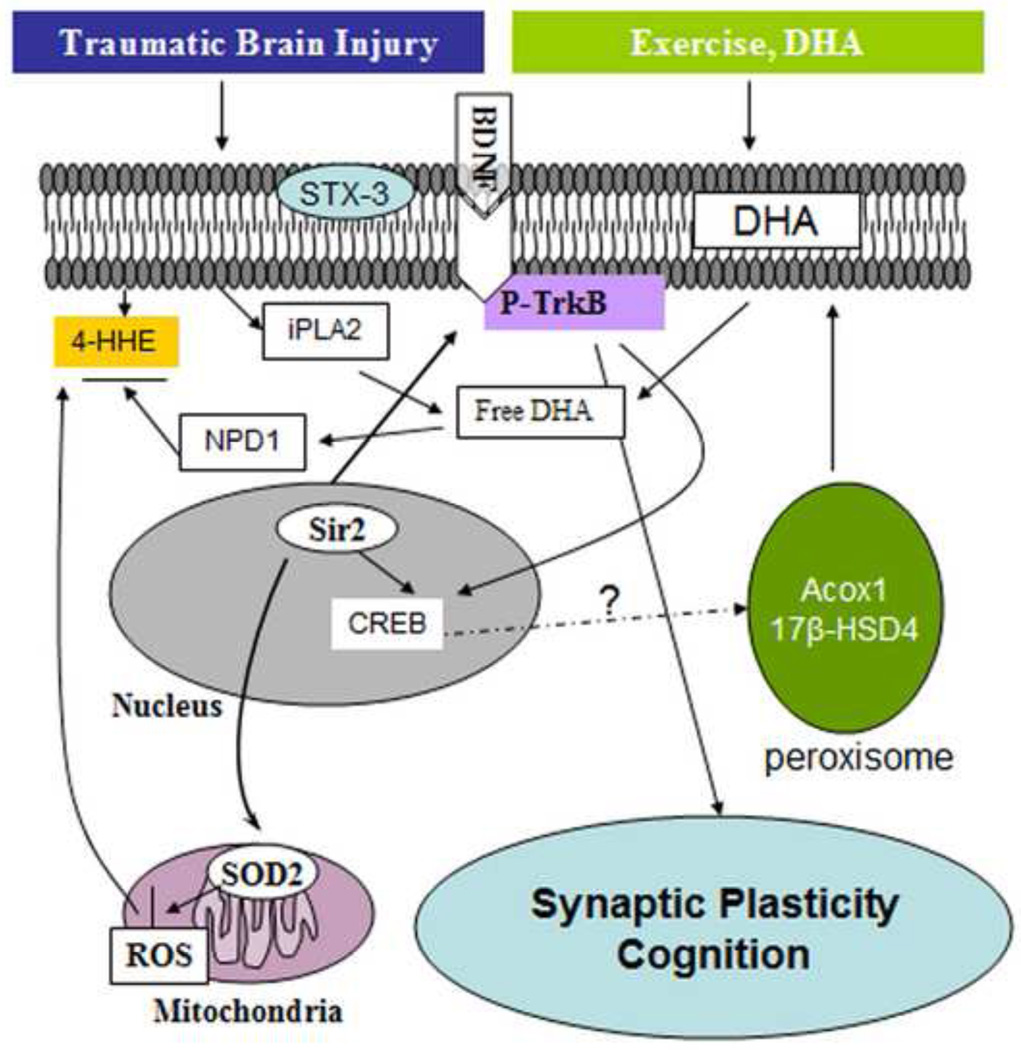
Figure 7.
Possible mechanisms underlying the beneficial effects of exercise and DHA supplementation on cognitive improvement after TBI. Exercise can complement the action of DHA supplementation to maintain DHA levels in the plasma membrane by acting on the enzymes Acox1 and 17 -HSD4, which regulate DHA synthesis. The action of diet and exercise can also be exerted on maintaining membrane homeostasis by reversing the action of TBI on reducing iPLA2 and STX-3. Exercise and DHA can increase resistance to oxidative damage (i.e. reduction of 4-HHE and increase of Sir2). These beneficial effects may help activate BDNF-TrkB signaling, subsequently improving cognitive function after train trauma.