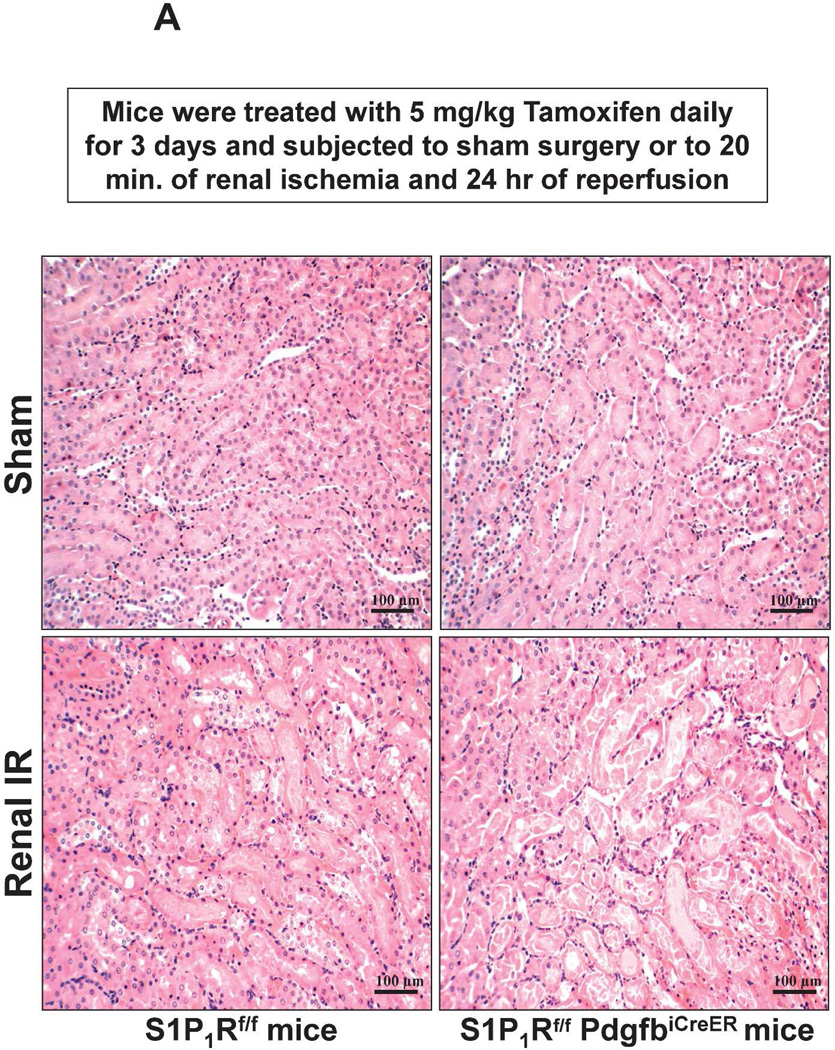
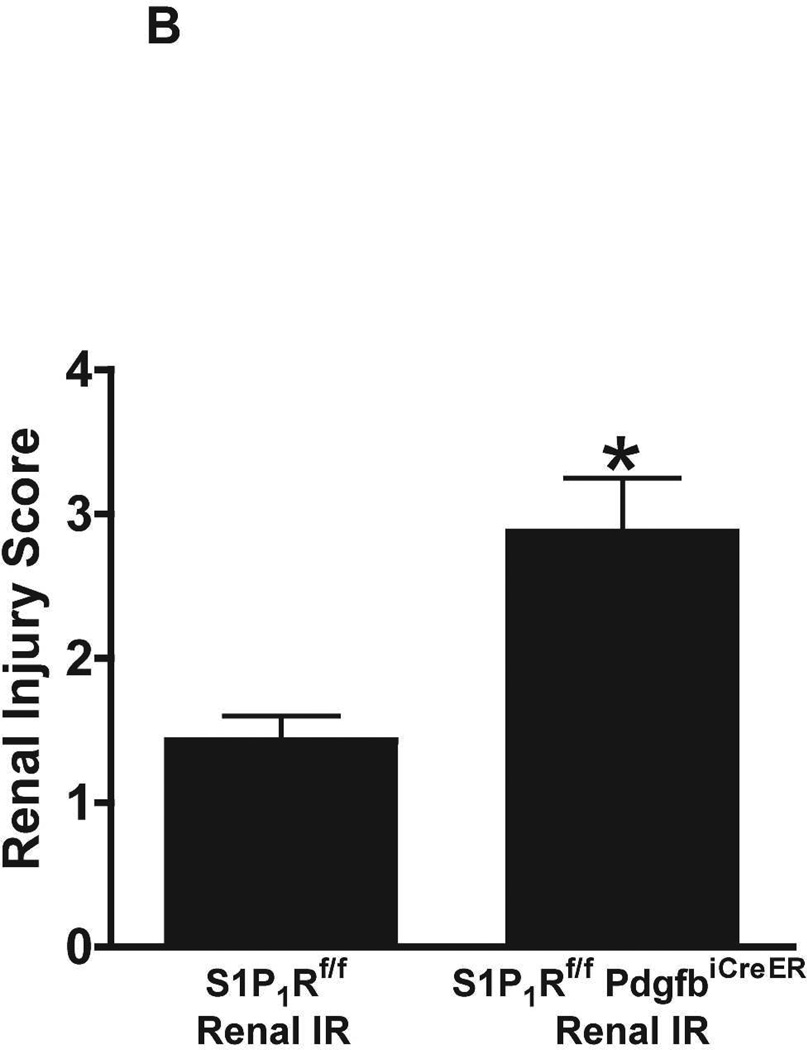
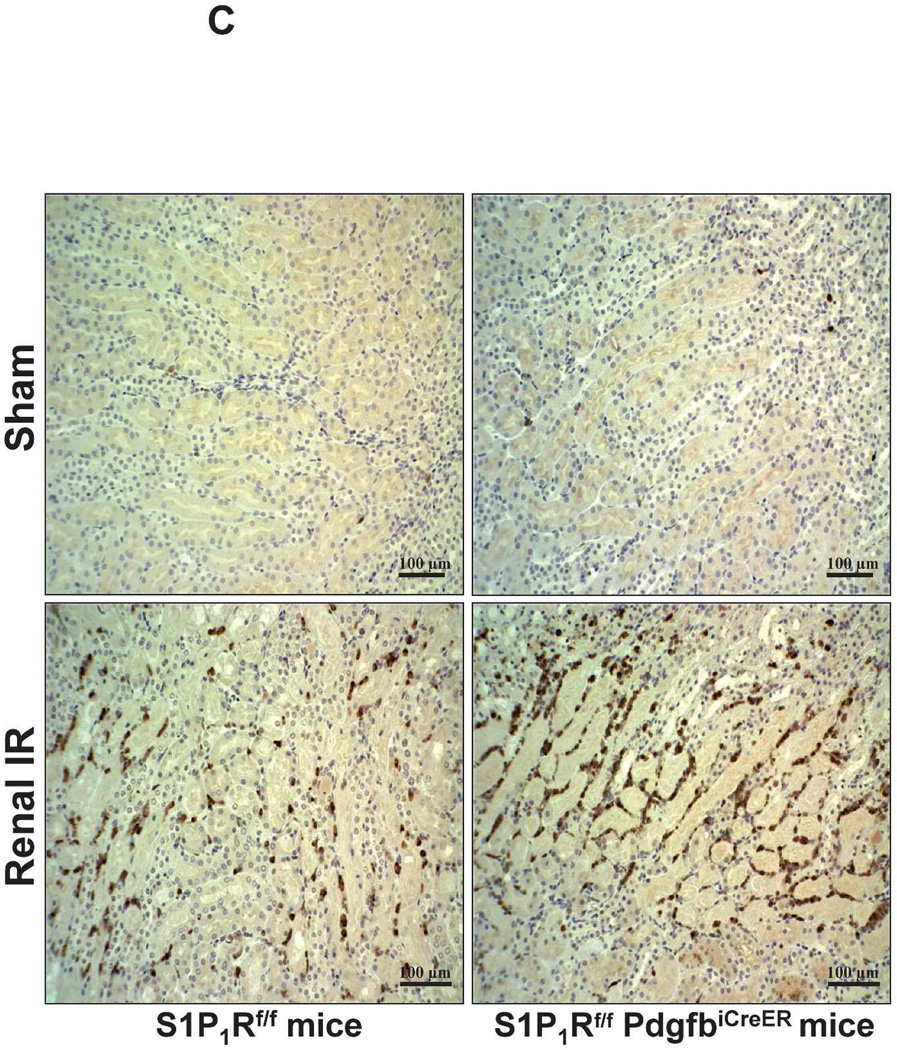
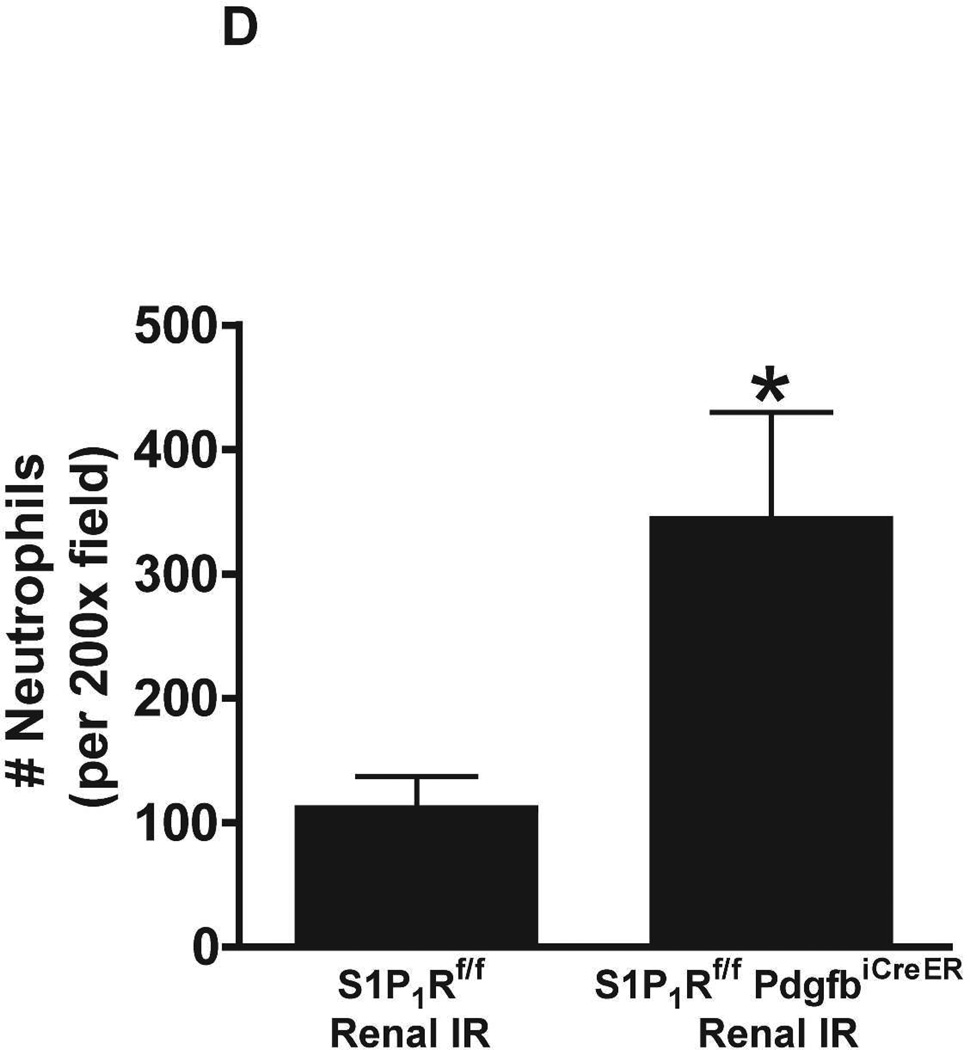
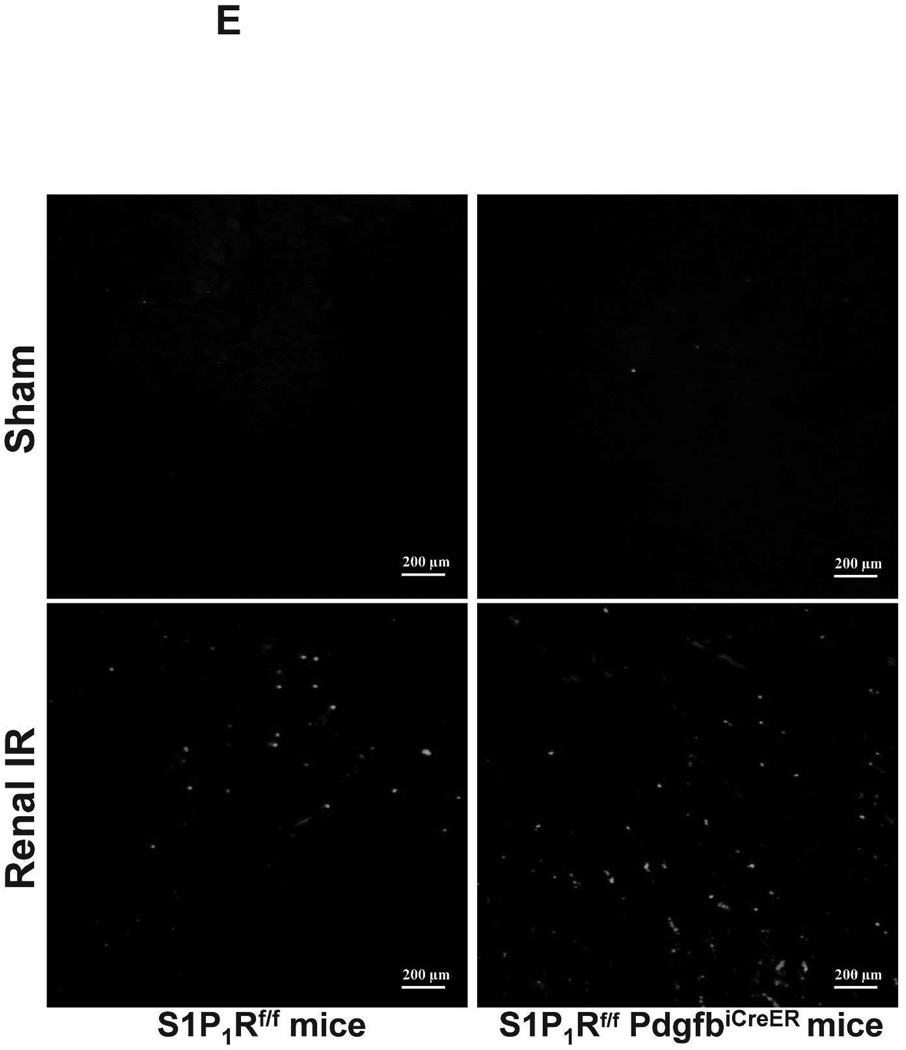
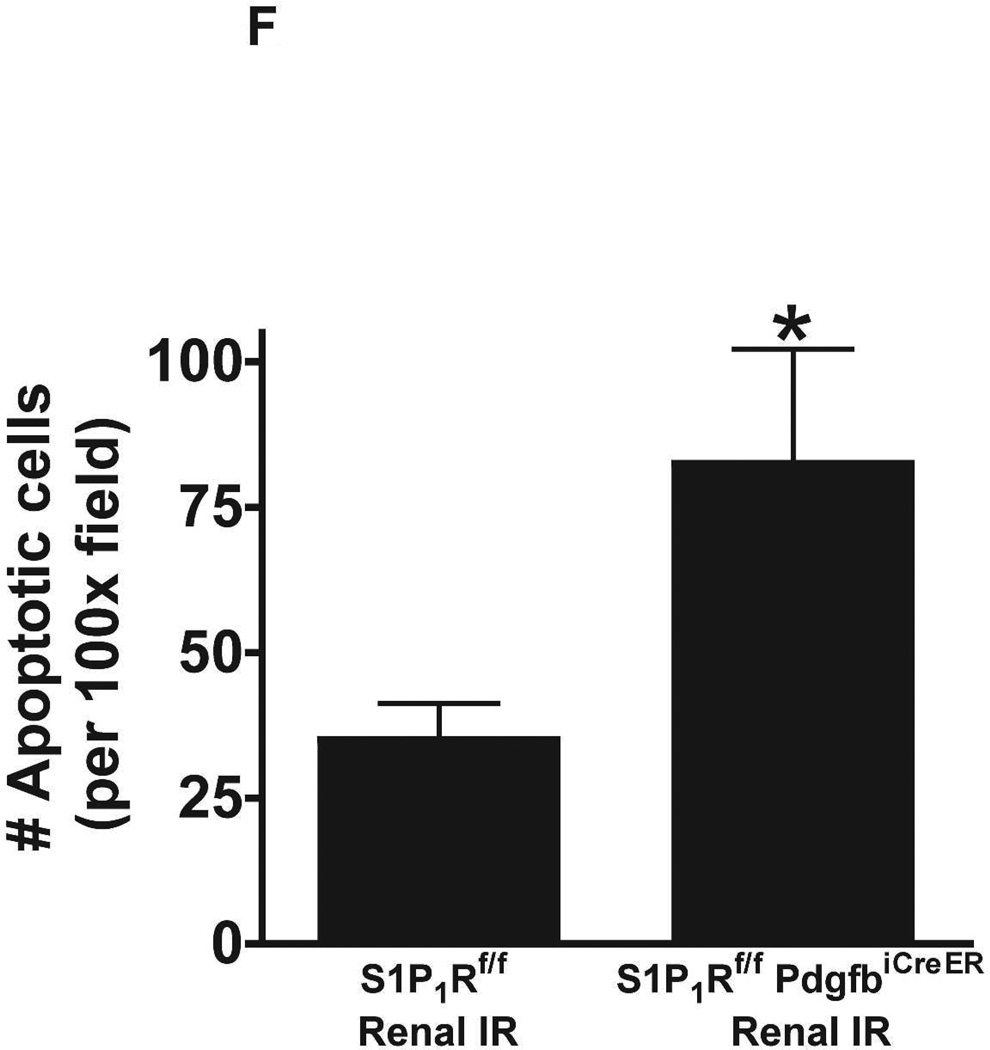
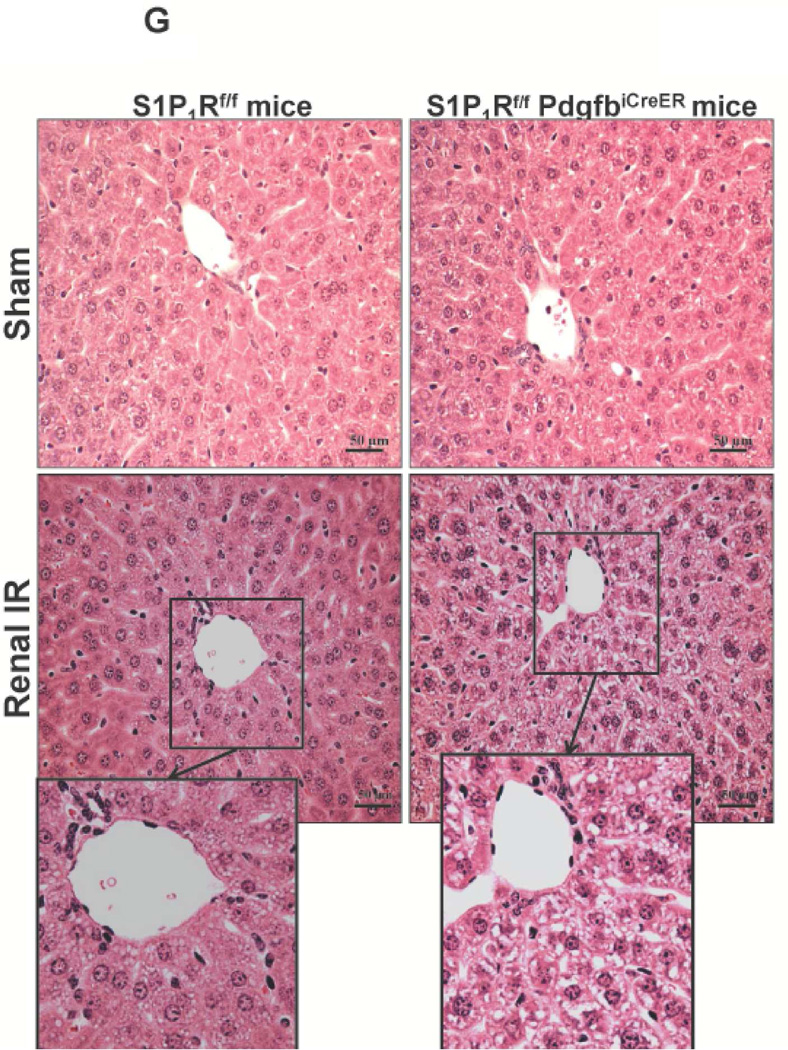
Figure 5. Endothelial S1P1R deletion increases renal necrosis, neutrophil infiltration and apoptosis as well as hepatic vacuolization after renal IR.
A. Representative hematoxylin and eosin staining (magnification 200X) of kidney sections of tamoxifen-treated (5 mg/kg i.p. daily for 3 days) endothelial S1P1R null (S1P1Rf/f PdgfbiCreER) mice or wild type (S1P1Rf/f) mice subjected to sham-operation or to 20 min of renal ischemia and 24 hr of reperfusion. Photographs are representative of 6 independent experiments. B. Summary of Jablonski scale renal injury scores (scale 0–4) for mice subjected to renal IR. Tamoxifen-treated wild type (S1P1Rf/f) mice showed increased renal tubular necrosis after renal IR. Endothelial S1P1R deficiency further exacerbated renal tubular necrosis in mice subjected to renal IR injury. C and E. Representative photomicrographs for immunohistochemistry (brown staining) for neutrophil infiltration (C, magnification 200X) and TUNEL staining (E, representing apoptotic nuclei, magnification 100X) from kidneys of tamoxifen-treated endothelial S1P1R null (S1P1Rf/f PdgfbiCreER) mice or wild type (S1P1Rf/f) mice subjected to sham-operation or to 20 min of renal ischemia followed by 24 hr of reperfusion (IR). Tamoxifen-treated wild type mice showed extensive neutrophil infiltration and TUNEL positive cells after 20 min of renal IR. Tamoxifen-treated endothelial S1P1R null (S1P1Rf/f PdgfbiCreER) mice had increased neutrophil infiltration after renal IR. Few neutrophils were also visible in tamoxifen-treated sham-operated endothelial S1P1R null mice. D and F. Quantifications of infiltrated neutrophils per 200X field (D, N=4–6) and apoptotic cells per 100X field (F, N=5) in the kidneys of tamoxifen-treated endothelial S1P1R null (S1P1Rf/f PdgfbiCreER) mice or wild type (S1P1Rf/f) mice subjected to 20 min of renal ischemia followed by 24 hr of reperfusion. *P<0.05 vs. S1P1Rf/f mice subjected to renal IR. Error bars represent 1 SEM. G. Liver histology was assessed by H&E staining (representative of 5–6 slides, 400X). Sham-operated wild type mice had normal liver histology. Twenty min of renal ischemia and 24 hr of reperfusion resulted in mild to moderate nuclear and cytoplasmic degenerative changes, cellular vacuolization, congestion as well as individual hepatocyte necrosis and focal apoptotic, pyknotic nuclei were observed. The severity of liver injury was increased for conditional endothelial S1P1R deficient mice manifested by increased of cellular degenerative changes including increased individual hepatocyte necrosis, apoptosis and vacuolization.