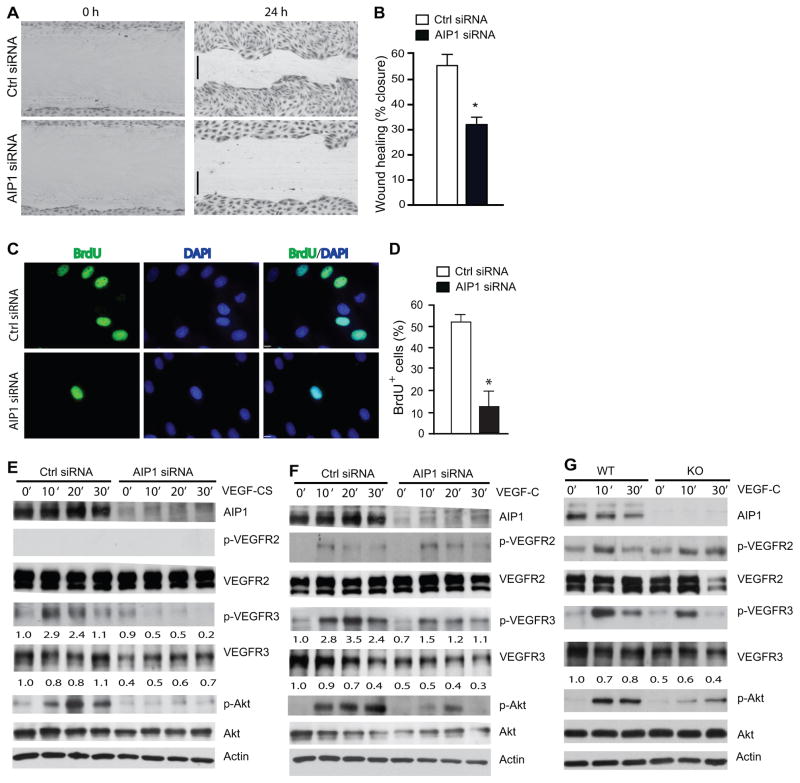
Figure 6. AIP1 mediates VEGF-C-induced lymphangiogenic signaling.
A–B. HLEC monolayer migration assay. 48 h after transfection with Ctrl or AIP1 siRNA, confluent monolayers of HLEC were subjected to “wound” injury assay in the presence of 3% serum + VEGF-CS (250 ng/ml) for 24 h. Representative images are shown in A. Scale bar, 100 μm. Cell migration distances (mm) were measured and % wound closure was quantified in B. Data are mean±SEM from duplicates (10 different areas in each well) of three independent experiments. *, P<0.05. C–D. BrdU incorporation assay. 48 h after transfection with Ctrl or AIP1 siRNA, HLEC were subjected to BrdU labeling for 4 h followed by immunostaining with anti-BrdU. Representative images are shown in C and BrdU+ cells were quantified in D. Data are mean±SEM from duplicates (5 different areas in slide) of three independent experiments. *, P<0.05. E–F. Effects of AIP1 knockdown in VEGF-CS- and VEGF-C signaling. HLEC were transfected with a human AIP1 siRNA or control siRNA (20 nM) for 24 h, subsequently serum-starved overnight. Cells were treated with VEGF-CS (250 ng/ml) or VEGF-C (100 ng/ml) for indicated times. Knockdown of AIP1 was determined by Western blot with anti-AIP1. Phosphorylations of VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3 and Akt were determined by Western blot with phosphor-specific antibodies. Total levels of VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3 and Akt were determined by Western blot with respective antibodies. β-actin was used as a loading control, and relative levels of p-VEGFR-3 and total VEGFR-3 are indicated below the blot with untreated Ctrl group as 1.0. Similar results were obtained from additional two experiments. G. Effects of AIP1 deletion on VEGF-C signaling. Mouse dermal lymphatic EC were isolated. Cells were cultured and treated with VEGF-C as in F for indicated times. Phosphorylations of VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3 and Akt were determined by Western blot with phosphor-specific antibodies. Total protein levels of VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, Akt and AIP1 were determined by Western blot with respective antibodies. Similar results were obtained from additional two experiments.