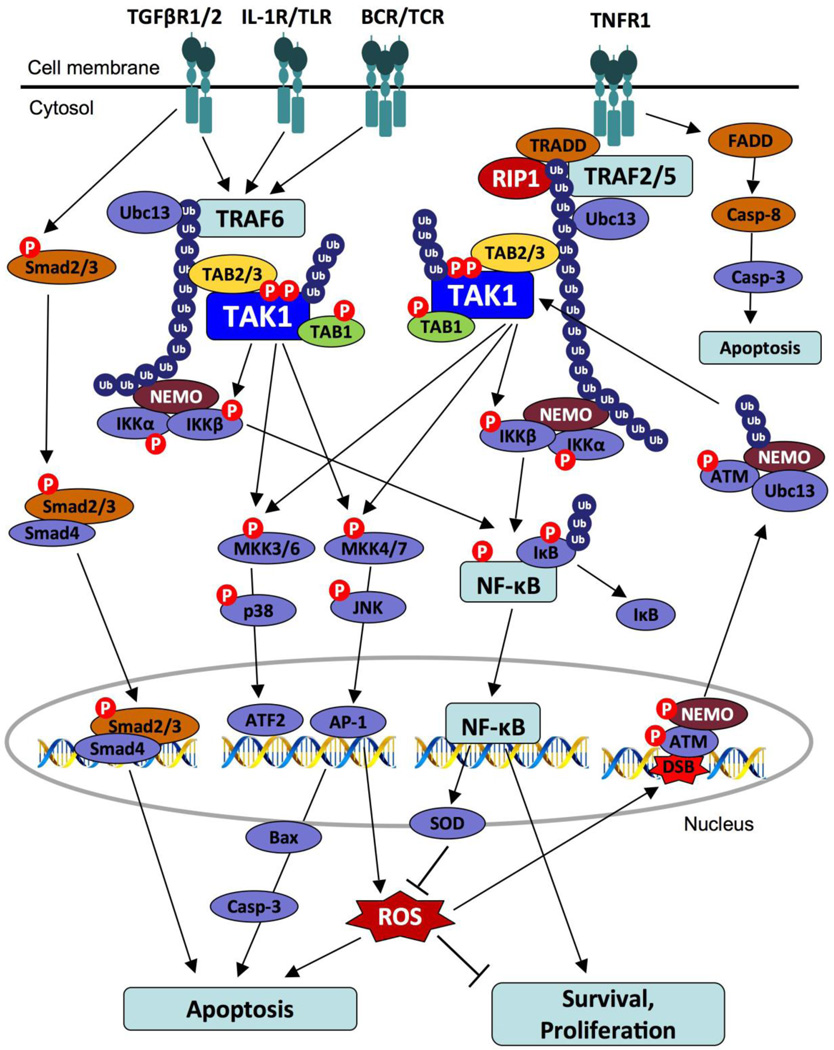
Figure 2. Activation of TAK1 Signaling.
(1) Binding of TNF to the TNFR type 1 leads to the formation of complex comprising TRADD, RIP1, TRAF2/5, and Ubc13. K63 ubiquitination of RIP1 recruits and activates TAK1 through TAB2. (2) IL-1R, TLR, TGF-β, TCR, and BCR utilize TRAF6 and Ubc13 to create K63 polyubiquitin chains that recruit TAB2 of TAK1 complex. (3) TAK1 phosphorylates and activates the IKK complex, leading to the phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and degradation of IκBα. The freed NF-κB is activated and translocated into nucleus. (4) MAPK pathways are activated in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. (5) DNA double-strand breaks (DSB) induce sumoylation and monoubiquitination of NEMO that interacts with ATM. NEMO-ATM complex promotes K63 polyubiquitination by Ubc13, which in turn activates TAK1 and IKK.