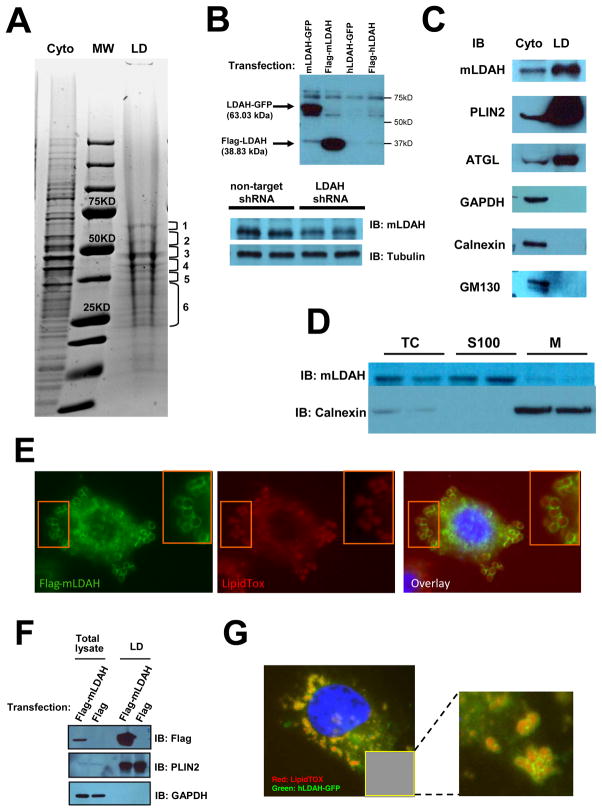
Figure 1. Identification of a novel candidate LD-associated CE hydrolase.
(A) LD proteins isolated from RAW 264.7 macrophages were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue. Six gel fragments containing most protein bands were analyzed by nano LC-MS/MS. Cyto= cytoplasmic fraction; LD= LD fraction; MW= molecular weight marker. (B) A custom anti-mLDAH antibody was generated, and its specificity was confirmed in HeLa cells transfected with mouse and human LDAH-GFP and flag-LDAH, and in RAW 264.7 macrophages with shRNA-mediated mLDAH downregulation. (C) Immunoblot with anti-mLDAH on the cytosolic and LD fractions that were used for the proteomic analysis. Immunoblots with antibodies against GAPDH (cytoplasmic protein), calnexin (ER protein), GM130 (Golgi protein), and PLIN2 and ATGL (LD proteins) verified the purity of the LD fraction. (D) Immunoblot with anti-mLDAH performed on total cytosol (TC), soluble 100,000 × g fractions (S100), and 100,000 × g membrane pellets (M) of RAW 264.7 macrophages. (E) Immunostaining with anti-flag (green) on acLDL-treated (50 μg/ml, 18h) RAW 264.7 macrophages transfected with flag-mLDAH. LipidTox™ (red) was used to stain LDs. (F) Immunoblot with anti-flag on total lysate and LD fractions of flag-mLDAH-transfected HeLa cells treated with oleic acid (360 μM, 18h). (G) Fluorescence microscopy on HeLa cells transfected with hLDAH-GFP (green) and treated with oleic acid (360 μM, 18h). LipidTOX™ was used to label LDs (Red).