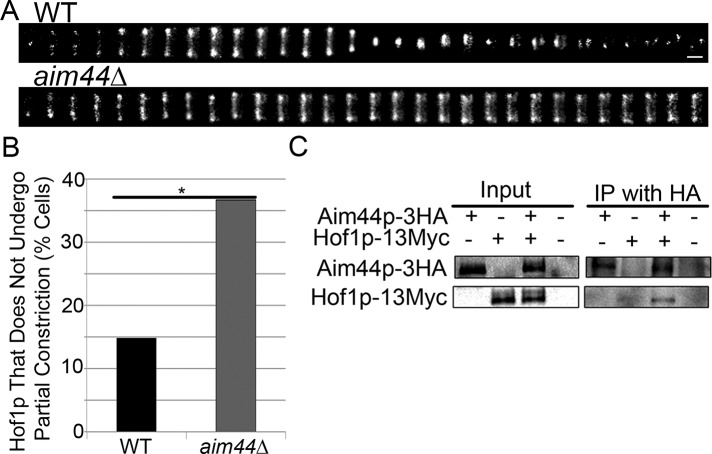
FIGURE 7:
Aim44p regulates Hof1p localization and dynamics at the bud neck and coimmunoprecipitates with Hof1p. (A) Wild-type and aim44Δ cells expressing Hof1p-GFP were synchronized as for Figure 6. Hof1p-GFP were imaged every 5 min beginning 60 min after release from G1 arrest for a total time of 3 h. Montages showing changes in Hof1p localization and dynamics at the bud neck as a function of time after release from pheromone-induced G1 arrest in wild-type cells (top) and aim44∆ mutants (bottom). Scale bar, 0.3 μm. (B) Quantitation of wild-type and aim44∆ cells that exhibit Hof1p-GFP ring contraction (p = 0.0003, chi-squared test). n = 101 and 120 for wild-type and aim44∆ cells, respectively. Data are pooled from two independent experiments. (C) Yeast cells expressing no tagged proteins, Aim44p-3HA, Hof1p-13Myc, or both Aim44p-3HA and Hof1-13Myc were grown to mid log phase and treated with pheromone as for Figure 1. Whole-cell extracts were prepared from each sample 75 min after release from pheromone-induced G1 arrest, and samples were immunoprecipitated using anti-HA antibodies. Western blots show whole-cell extracts and immunoprecipitated proteins detected using anti-HA and anti-Myc antibodies. Hof1p-Myc coimmunoprecipitates with Aim44p-HA.