FIGURE 5.
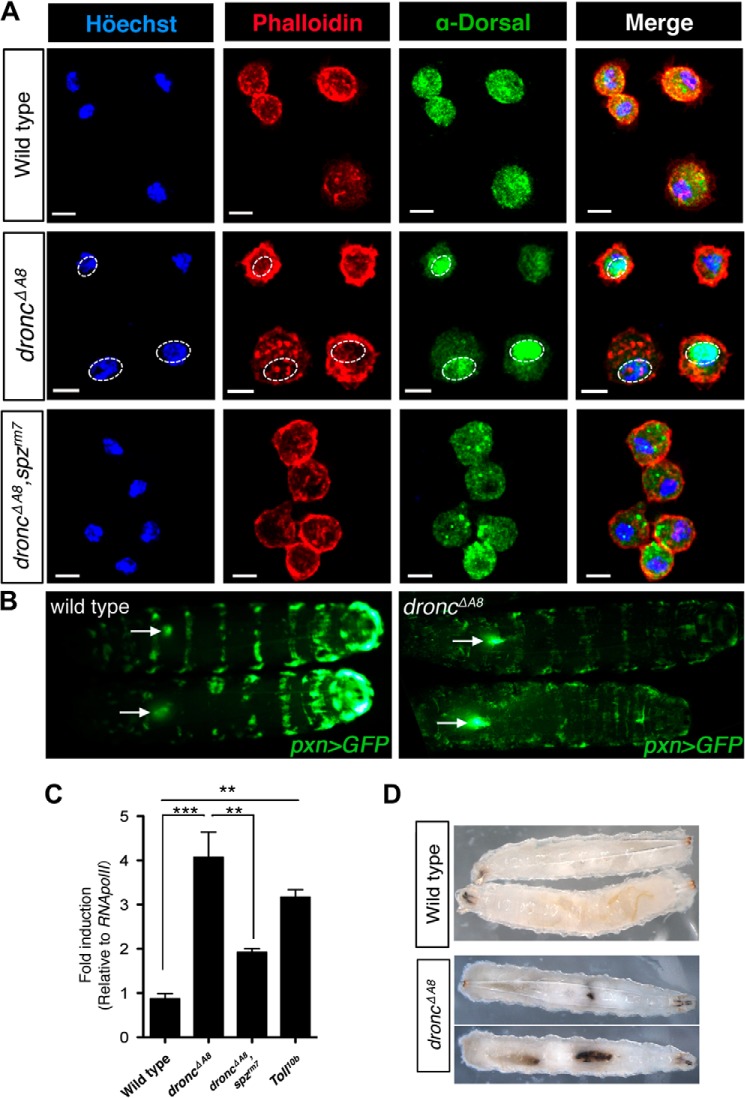
droncΔA8 mutants exhibit hematopoietic disorders and random formation of melanotic clots. A, Spätzle mediates Dorsal nuclear translocation in circulating hemocytes from droncΔA8 mutants. The nuclei (cyan) and cell periphery (red) were visualized by staining with Höechst 33342 and rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin, respectively. Immunohistochemical staining showed the nuclear accumulation of Dorsal (green) in droncΔA8 mutants, whereas the loss of spz abrogated this phenotype. The genotype for each row is indicated at left. Scale bar, 5 μm. B, visualization of lymph gland hypertrophy. Images show GFP fluorescence from the dorsal side. The arrows point to lymph glands containing GFP-expressing hemocytes, with the arrowheads oriented toward the posterior end of the larvae. The genotypes were pxn-Gal4, UAS-GFP for wild type and pxn-Gal4, UAS-GFP; droncΔA8/droncΔA8 for droncΔA8 mutants. C, quantitative RT-PCR analysis of hemese, a pan-hemocyte marker in Drosophila (32, 57) indicated that droncΔA8 mutants have increased total blood cell numbers, comparable to the level observed in Tl10b mutants. The data show means ± S.E. Statistics are results of one-way analysis of variance test. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.0001. D, induction of a melanotic tumor in droncΔA8 flies.