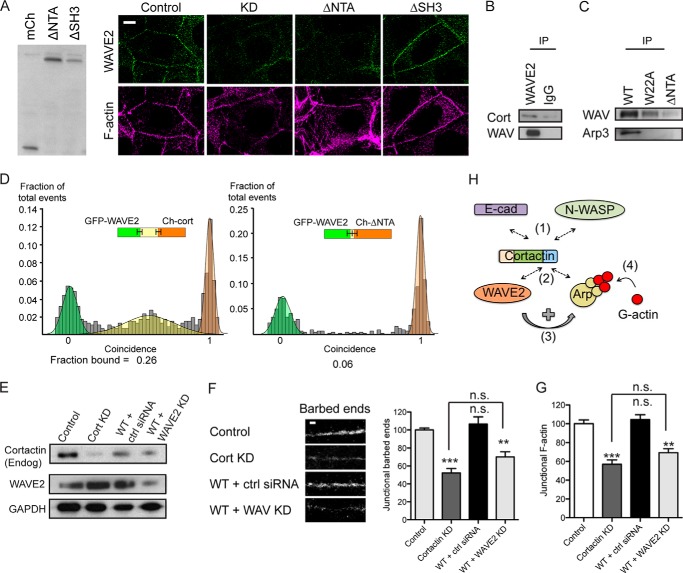
FIGURE 7.
WAVE2 can interact with the N terminus of cortactin. A, characterization of control cells, cortactin KD cells, and KD cells reconstituted with cortactin ΔNTA or ΔSH3 mutants. Immunoblots of cell lysates were probed for mCherry (left panel); all cortactin mutants ran at the expected molecular mass. Representative confocal images were stained for WAVE2 and F-actin (right panel). Junctional WAVE2 was lost from the contacts (marked by F-actin staining) in cortactin KD and ΔNTA cells but restored by ΔSH3 cortactin. B, WAVE2 immunoprecipitates (IP) from Caco-2 cell lysates probed for cortactin (Cort) and WAVE2. C, cell lysates from cortactin KD cells expressing GFP-tagged wild-type cortactin (WT), W22A mutant, or ΔNTA mutant were immunoprecipitated with anti-GFP antibody and immunoblotted for WAVE2 and Arp3. The W22A mutant could co-immunoprecipitate WAVE2 but not Arp3, whereas the ΔNTA mutant could pull down neither protein. D, direct interactions between in vitro translated WAVE2 and cortactin assessed by single molecule coincidence analysis. WAVE2 interacted with full-length cortactin but not with the ΔNTA mutant. E–G, cortactin knockdown cells reconstituted with wild type (WT) cortactin were transfected with nontargeting siRNA (+ ctrl siRNA) or siRNA targeted against WAVE2 (+ WAVE2 KD). E, Western analysis of whole cell lysates immunoprobed for cortactin (endogenous (Endog)), WAVE2, and GAPDH as a loading control (left panel). F, representative images of barbed end labeling at junctions in cell lines (left panel) and quantitation of junctional barbed end labeling (right panel). G, quantitation of junctional F-actin. (n = 48–60 contacts pooled from 4 to 5 independent experiments). Scale bar is 10 μm in A and 2 μm in F; data are means ± S.E.; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001; n.s., not significant. H, conceptual model of cortactin as a coincident scaffold that regulates actin nucleation at the ZA. Cortactin binds directly to β-catenin-bound E-cadherin at the ZA via an N-WASP-dependent mechanism (bar 1). The N-terminal acidic domain of cortactin recruits both Arp2/3 and WAVE2 (bar 2), whereupon WAVE2 activates Arp2/3 (bar 3) to promote actin nucleation and polymerization at the ZA (bar 4).